If you’re struggling with persistent tiredness that won’t improve despite adequate rest, you’re not alone. We understand the frustration of feeling drained when you have responsibilities to meet and life to enjoy. You’ve found the right resource to explore whether IV therapy could be the energy-boosting solution you’ve been searching for.
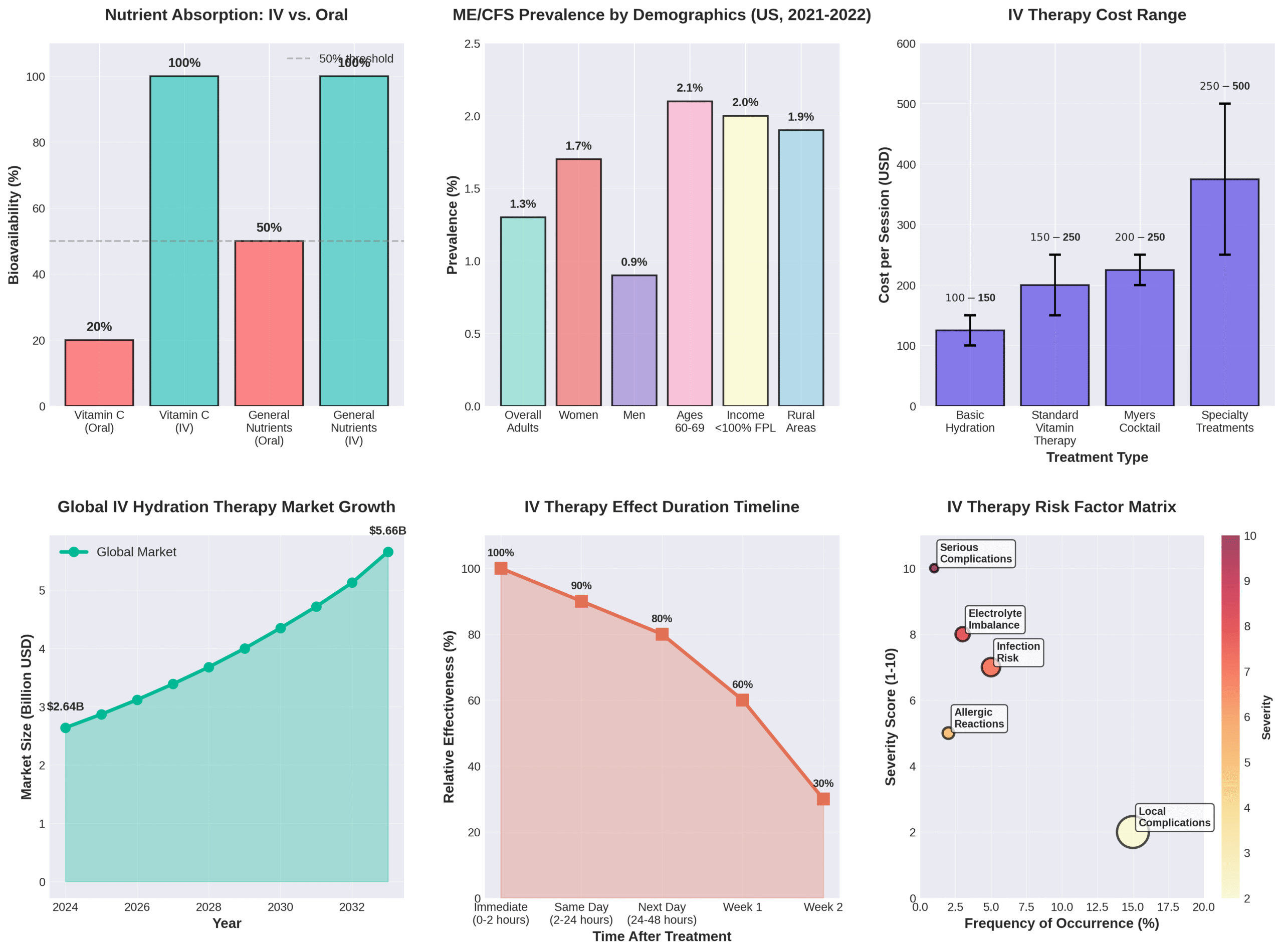
Fatigue is the main reason or a secondary reason for 10-20% of patient consultations in primary care. This widespread condition affects productivity, quality of life, and overall well-being for millions of people. Intravenous (IV) therapy delivers vitamins, minerals, and hydration directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system entirely to achieve 100% bioavailability of nutrients—a significant advantage over oral supplements that typically achieve only 20-50% absorption.
According to a 2012 study published in Nutrition Journal, administration of high dose intravenous vitamin C reduced fatigue significantly compared to placebo in office workers, with effects persisting for one day. The controlled trial demonstrated both the safety and effectiveness of this approach for combating workplace fatigue.
Dr. Ali and colleagues from Yale University noted in their pioneering 2009 study: “Most subjects experienced relief compared to baseline” when treating fibromyalgia patients with intravenous micronutrient therapy, establishing both safety and feasibility of the treatment approach.
Key Takeaways:
• Sleep disorders, depression (18.5% of cases), and excessive psychosocial stress are the most common causes of persistent fatigue
• IV therapy achieves 90-100% bioavailability compared to 20-50% for oral supplements
• Standard Myers’ Cocktail contains magnesium, B-complex vitamins, vitamin C, and other nutrients specifically targeting fatigue
• Results typically last from several days to a few weeks after treatment
• 82% of chronic fatigue patients receiving iron IV therapy reported better energy levels versus 47% with placebo
• Treatment sessions cost $100-$500 depending on formulation and provider
High-Level Overview: This comprehensive guide examines how IV therapy addresses fatigue through direct nutrient delivery, exploring the science behind various formulations, identifying ideal candidates, and comparing effectiveness to traditional treatments. We’ll analyze research-backed benefits, potential risks, and cost considerations while providing practical insights for those considering IV therapy at The Drip IV Infusion.
Practical Tip: Before pursuing IV therapy, document your fatigue patterns for 1-2 weeks, noting energy levels throughout the day, sleep quality, and any activities that worsen symptoms. This information helps healthcare providers customize your IV formulation for optimal results.
As we explore the intricate relationship between nutrient deficiencies and fatigue, we’ll uncover why direct intravenous delivery might succeed where oral supplements have failed, setting the stage for understanding this innovative approach to restoring your vitality.
What Causes Fatigue and How Is It Typically Treated?
Fatigue drives 10-20% of primary care consultations, affecting approximately 10% of the general population with chronic symptoms. Sleep disorders remain the most common culprit for persistent fatigue, while depression accounts for 18.5% of cases and excessive psychosocial stress ranks among leading causes. Between 836,000 to 3.3 million Americans have myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), with prevalence reaching 1.3% of adults in 2021-2022.
Women and older adults show higher ME/CFS rates, peaking at ages 60-69. Unexplained fatigue affects 4.1% of the population—2.7 times more common than explained fatigue. Cancer patients rank fatigue as their most distressing symptom 60% of the time, while undiagnosed cancer causes only 0.6% of persistent fatigue cases. This section examines fatigue’s medical and lifestyle causes, then compares traditional treatments to IV therapy’s direct nutrient delivery approach.
What Are the Most Common Medical and Lifestyle Reasons for Fatigue?
The most common medical and lifestyle reasons for fatigue are sleep disorders, depression, psychosocial stress, and chronic diseases. Primary care data shows fatigue appears in 10-20% of consultations as either a main or secondary complaint. Sleep-related breathing disorders top the list of persistent fatigue causes. Depression contributes to 18.5% of persistent fatigue cases, while excessive psychosocial stress ranks equally high.
Chronic fatigue syndrome affects a significant portion of Americans. There are 836,000 to 3.3 million people with ME/CFS in the United States. Women experience higher ME/CFS prevalence than men. Adults aged 60-69 show peak ME/CFS likelihood. The total prevalence of unexplained fatigue reaches 4.1%, exceeding explained fatigue by 2.7-fold.
| Condition | Metric | Estimate | Source/Year |
| Primary care fatigue consultations | Percentage | 10-20% | Clinical data |
| Chronic fatigue | General prevalence | 10% | Population studies |
| Depression | Fatigue contribution | 18.5% | Medical records |
| ME/CFS | U.S. cases | 836,000-3.3 million | 2021-2022 |
| Unexplained fatigue | Prevalence | 4.1% | Epidemiological data |
| Cancer-related fatigue | Patient distress ranking | 60% most distressing | Patient surveys |
| Undiagnosed cancer | Fatigue cause percentage | 0.6% | Diagnostic studies |
| Anemia/organic causes | Fatigue contribution | 4.3% | Clinical analysis |
Multi-morbidity increases severe fatigue odds in chronic disease patients. Traditional treatments must address these diverse underlying causes to effectively combat fatigue symptoms.
How Do Traditional Treatments for Fatigue Compare to IV Therapy?
Traditional treatments for fatigue compare to IV therapy through stark differences in absorption rates and bioavailability. Oral supplements achieve 20-50% absorption while IV vitamins reach 100% absorption directly into the bloodstream. Gastric acidity, digestive enzymes, gut microbiota, and underlying conditions significantly affect oral supplement absorption. Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, IBS, and malabsorptive disorders frequently hinder nutrient uptake through the digestive tract.
Vitamin C illustrates absorption limitations clearly. Oral vitamin C intake exceeding one gram results in diminished absorption due to limited intestinal transporter capacity. Daily oral intake of 200-400 mg saturates blood levels in healthy individuals. IV therapy achieves 90% bioavailability compared to oral supplements’ typical 20% bioavailability.
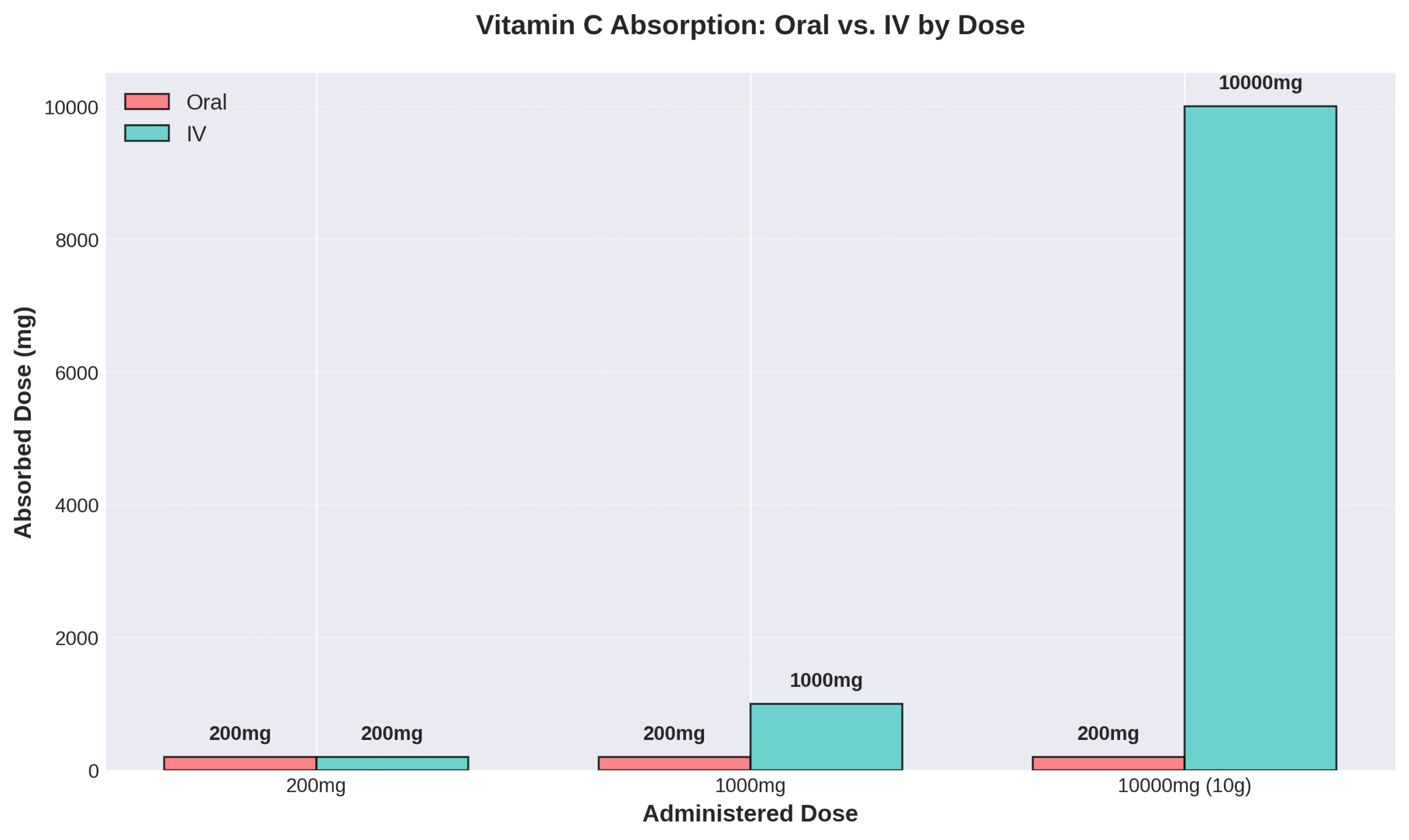
The Mayo Clinic notes limited evidence exists for IV vitamin benefits in people with normal nutritional intake and levels. This comparison sets the foundation for understanding when IV therapy offers advantages over traditional oral supplementation for fatigue management.
What Is IV Therapy and How Does It Work for Fatigue?
IV therapy is a medical treatment that delivers vitamins, minerals, and fluids directly into the bloodstream through an intravenous drip. This method bypasses the digestive system entirely, allowing nutrients to achieve 100% bioavailability compared to the 20-50% absorption rates of oral supplements. The direct infusion enables rapid cellular uptake with immediate physiological benefits for fatigue relief.
The Drip IV Infusion provides specialized formulations that target fatigue through precise nutrient combinations. These treatments deliver therapeutic doses of B-complex vitamins, vitamin C, magnesium, and amino acids directly to cells where energy production occurs. The following subsections detail the specific ingredients, delivery mechanisms, and scientific evidence supporting IV therapy for fatigue management.
What Ingredients Are Used in IV Therapy Formulas for Fatigue?
The ingredients in IV therapy formulas for fatigue include vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and specialized compounds designed to boost energy production. Standard Myers’ Cocktail formulation contains 5 mL magnesium chloride hexahydrate (20%), 3 mL calcium gluconate (10%), 1 mL hydroxocobalamin (1,000 μ/mL), 1 mL pyridoxine hydrochloride (100 mg/mL), 1 mL dexpanthenol (250 mg/mL), 1 mL B-complex 100, 5 mL vitamin C (500 mg/mL), and 20 mL sterile water.
Energy-boosting formulas contain vitamin B12 and magnesium, which contribute to the reduction of tiredness and fatigue. Amino acid blends incorporate B-complex, vitamin B12, L-glutathione, zinc, magnesium, L-carnitine, and various amino acids essential to muscle restoration. High-dose vitamin C therapy uses doses between 25-50 grams intravenously.
| Infusion Type | Key Component | Composition |
| Myers’ Cocktail | Magnesium content | 5 mL at 20% concentration |
| Myers’ Cocktail | Vitamin C dose | 2,500 mg total |
| Energy formulas | Key ingredients | B12, magnesium, amino acids |
| High-dose vitamin C | Therapeutic range | 25-50 grams |
| Performance blends | Components | Amino acids, B vitamins, recovery compounds |
Wellness boost formulas contain balanced blends of B-complex vitamins, vitamin C, magnesium, and essential minerals. Immune defense formulas incorporate high-dose vitamin C, zinc, selenium, and other immune-supporting nutrients specifically formulated to combat fatigue associated with immune system stress.
How Does IV Therapy Deliver Nutrients Differently Than Oral Supplements?
IV therapy delivers nutrients differently than oral supplements by achieving virtually 100% bioavailability through direct entry into systemic circulation. Nutrients administered intravenously circumvent hepatic first-pass metabolism, a significant limitation of oral supplements. IV vitamins work almost instantly while oral vitamins require digestive processing.
IV administration bypasses saturable absorption mechanisms, virtually removing the upper limit of maximum achievable plasma concentration. High-dose vitamin C delivered intravenously achieves plasma levels up to 100 times higher than those achieved orally. A linear relationship exists between dose and Cmax for IV doses up to 70 g/m2 in humans, resulting in plasma concentrations of approximately 50 mM.
Key delivery differences include:
- Complete bypass of digestive system barriers
- Immediate systemic circulation entry
- No degradation from stomach acid or enzymes
- Avoidance of GI side effects such as osmotic diarrhea
- Direct cellular uptake without transporter limitations
The direct delivery method ensures rapid cellular uptake with immediate physiological benefits that oral supplements cannot match due to absorption limitations.
What Is the Scientific Basis for Using IV Therapy to Address Fatigue?
The scientific basis for using IV therapy to address fatigue rests on clinical studies demonstrating measurable improvements in energy levels and fatigue reduction. A controlled pilot study of Myers’ Cocktail for fibromyalgia established safety and feasibility with most subjects experiencing relief compared to baseline. High-dose intravenous vitamin C proved safe and effective against fatigue, reducing fatigue at two hours with effects persisting for one day.
Research outcomes supporting IV therapy efficacy include an iron IV therapy study where 82% of patients reported better energy levels compared to only 47% with placebo. A comprehensive review of 35 studies investigating L-carnitine and CoQ10 for fatigue symptoms found most reporting statistically significant positive outcomes. IV saline infusion showed substantial beneficial effects in a subgroup of patients with ME/CFS.
| Compound | Outcome Measure | Reported Result | Source |
| Iron IV therapy | Energy improvement rate | 82% vs 47% placebo | Clinical trial |
| Vitamin C IV | Fatigue reduction timeframe | 2 hours | Office worker study |
| L-carnitine/CoQ10 | Positive studies | 35 total reviewed | Systematic review |
| Myers’ Cocktail | Citation count | 86 publications | Pilot study |
Enhanced energy production associates with B-complex vitamins and magnesium delivered intravenously. Improved cognitive function and mental clarity result from vitamin B12, NAD+, and magnesium IV administration. IV glutathione and vitamin C significantly reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, addressing underlying causes of fatigue at the cellular level.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for IV Therapy for Fatigue?
Ideal candidates for IV therapy for fatigue include individuals with malabsorption disorders, chronic fatigue conditions, and those experiencing nutrient deficiencies that cannot be adequately addressed through oral supplementation. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, gastroparesis, or altered gut anatomy following bariatric surgery frequently face challenges maintaining optimal nutrient status through oral supplements alone. Athletes engaged in strenuous physical activities benefit from IV supplementation of amino acids, B vitamins, and magnesium for muscle recovery and energy metabolism. Understanding eligibility criteria, contraindications, and professional assessment processes helps determine whether IV therapy suits specific health needs.
Are There Certain Health Conditions or Symptoms That Respond Best?
The health conditions that respond best to IV therapy for fatigue are malabsorption disorders, chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, and vitamin B12 deficiency-related neurological complications. Patients with IBD, celiac disease, gastroparesis, or post-bariatric surgery anatomy benefit significantly because their compromised digestive systems prevent adequate nutrient absorption through oral routes. Individuals experiencing chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, or compromised immunity frequently report notable improvements in energy and overall well-being shortly after IV therapy sessions.
Neurological complications linked to vitamin B12 deficiency respond particularly well to IV administration. Cognitive impairment and peripheral neuropathy can be swiftly corrected through direct intravenous delivery of B12. Athletes and individuals engaged in strenuous physical activities see enhanced recovery through IV amino acids, B vitamins, and magnesium supplementation. Customized formulations like Myers’ Cocktail target diverse conditions including chronic fatigue, migraine headaches, and chronic stress. These targeted treatments address specific deficiency patterns and metabolic needs that standard oral supplementation cannot adequately resolve.
What Are the Contraindications or Reasons to Avoid IV Therapy?
The contraindications for IV therapy include risks of vitamin toxicity, electrolyte imbalances, allergic reactions, and lack of evidence for healthy individuals. Excessive administration of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K can accumulate in tissues and lead to toxic effects. Improper administration creates risks of electrolyte imbalances or fluid overload.
Allergic reactions represent another significant concern. These reactions can range from mild symptoms to severe anaphylaxis requiring immediate medical intervention. Limited evidence supports IV therapy benefits for healthy individuals in wellness contexts. The beneficial effects such as temporary increases in energy or hydration are usually transient and may not justify the risks or costs involved. Insurance coverage remains another practical barrier since IV therapy is rarely covered by health insurance plans. These factors make IV therapy unsuitable for individuals without specific medical indications or documented deficiencies.
How Is Eligibility for IV Therapy Determined by Professionals?
Eligibility for IV therapy is determined through personalized consultations, medical history assessments, and adherence to professional standards of care. The journey begins with a personalized consultation to assess health goals, medical history, and specific needs. Healthcare professionals combine essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and amino acids tailored to specific health requirements.
Professional standards mandate strict protocols for safe administration. IV therapy must be performed by qualified, licensed healthcare professionals following regulatory guidelines. The Oregon Medical Board requires licensees to ensure all IV Hydration Therapy treatments adhere to the same standards of care as any other medical treatments. Proper administration requires rigorous adherence to sterility protocols to minimize complications. Reputable med spas and infusion centers have protocols to confirm the contents of each IV bag before administration. Maintaining an aseptic technique throughout treatment is critical for safety. Each treatment is carefully formulated by teams of healthcare professionals who monitor patient responses and adjust protocols accordingly. This comprehensive assessment process ensures IV therapy is appropriate for individual circumstances and minimizes potential risks.
What Benefits and Results Can People Expect from IV Therapy for Fatigue?
IV therapy for fatigue delivers rapid nutrient absorption directly into the bloodstream, bypassing digestive limitations that reduce oral supplement effectiveness. The immediate bioavailability of vitamins, minerals, and amino acids through intravenous administration creates faster relief compared to traditional supplementation methods. Understanding the timeline and research supporting these benefits helps patients set realistic expectations for their treatment outcomes.
How Quickly Do Most People Feel Relief After an IV Drip?
Relief from IV therapy occurs within hours for many patients experiencing fatigue. A 2012 clinical trial demonstrated that intravenous vitamin C reduced fatigue at two hours in office workers, with participants reporting increased alertness immediately following treatment. Patients describe three common reactions to their first IV therapy session: feeling better, feeling no different, or feeling temporarily worse as the body adjusts.
The speed of relief depends on the specific nutrients administered and individual metabolic factors. Glutathione IV therapy produces noticeable improvements in mental clarity and focus shortly after infusion. B-complex vitamins and magnesium combinations generate energy boosts that patients feel during or immediately after their session.
Clinical observations show patients arriving with severe fatigue and malaise often leave treatment centers feeling energized and refreshed. The rapid onset occurs because nutrients bypass digestive processes and enter cells directly through the bloodstream. This immediate cellular uptake triggers metabolic processes that combat fatigue at the molecular level.
How Long Do the Effects of IV Therapy Typically Last?
The effects of IV therapy for fatigue typically last from several days to a few weeks after treatment. The 2012 vitamin C study found sustained fatigue reduction for one day following infusion, though many patients report longer-lasting benefits. Individual health status, nutrient deficiency levels, and lifestyle factors determine the duration of therapeutic effects.
Benefits continue developing over the days following treatment as cells utilize the infused nutrients. Patients receiving EBO2 therapy report gradual but significant energy improvements, with fatigue lifting progressively rather than suddenly. The sustained effect occurs because IV therapy replenishes cellular nutrient stores that support ongoing energy production.
Treatment frequency recommendations vary based on individual response patterns. Some patients maintain optimal energy with monthly sessions, while others benefit from bi-weekly treatments during periods of increased stress or fatigue. The cumulative effect of regular IV therapy often extends the duration of benefits between sessions.
Are the Results of IV Therapy for Fatigue Backed by Research?
Research supports IV therapy’s effectiveness for fatigue through multiple peer-reviewed studies. A systematic literature review assessed high-dose IV vitamin C’s impact on fatigue from various diseases, finding significant improvements across patient populations. The landmark Myers’ Cocktail pilot study has been cited by 86 publications, establishing the foundation for modern IV nutrient therapy protocols.
The office worker fatigue study using intravenous vitamin C has garnered 80-81 citations, demonstrating reproducible results in occupational health contexts. A comprehensive review of nutrient therapy for fatigue symptoms, cited by 30 publications, found that most studies reported statistically significant positive outcomes after treatment periods. The vitamin C pharmacokinetics study, with 1,264 citations, established the scientific basis for IV administration’s superior bioavailability.
Research consistently shows IV therapy achieves plasma nutrient concentrations impossible through oral supplementation. Studies document 100-fold higher vitamin C levels through IV administration compared to oral maximum absorption limits. This concentration difference translates to measurable clinical improvements in fatigue markers, energy production, and cellular function.
The growing body of evidence continues expanding as researchers investigate specific nutrient combinations and dosing protocols. Current studies focus on optimizing formulations for different fatigue etiologies and establishing standardized treatment guidelines. As IV therapy transitions from alternative to mainstream medicine, research quality and quantity continue improving, providing stronger validation for clinical applications in fatigue management.
What Potential Risks or Side Effects Exist With IV Therapy for Fatigue?
The potential risks or side effects of IV therapy for fatigue range from mild injection site discomfort to serious complications requiring immediate medical attention. A controlled study on vitamin C infusions found no significant differences in adverse events between treatment and control groups, indicating proper administration minimizes risks. Understanding these risks helps patients make informed decisions about IV therapy treatments.
What Are the Most Common Mild Reactions to IV Infusions?
The most common mild reactions to IV infusions are temporary discomfort at the injection site, nausea, and dizziness. Glutathione IV administration specifically causes nausea and dizziness in some patients. Vein-related complications occur frequently, including phlebitis, bruising, and potential vein damage or collapse from repeated infusions. These reactions typically resolve within hours to days without medical intervention. Patients receiving vitamin C infusions experience minimal side effects when protocols are properly followed.
Are There Serious Risks or Complications to Consider?
Serious risks of IV therapy include bloodstream infections, sepsis, and severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis. The FDA identified drug products compounded at medical offices prepared under insanitary conditions, increasing infection risk. A 2024 NPR report revealed no federal regulations exist for med spas offering IV therapy. California’s IV hydration clinics operate largely unregulated and fail to comply with national standards. Abscess formation occurs when sterility protocols are compromised during needle insertion or solution preparation. These complications require immediate medical attention and can result in hospitalization or death.
How Can Patients Minimize Their Risk When Receiving IV Therapy?
Patients minimize their risk by selecting facilities where certified healthcare professionals administer each session while monitoring comfort and safety throughout the 45-60 minute treatment. IV vitamin infusions prove generally safe when administered correctly following proper medical protocols. The FDA developed guidance documents for premarket notification submissions regarding IV administration sets to ensure equipment safety. Drug compounding in IV hydration clinics falls under Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, providing regulatory framework. Comfortable treatment rooms with relaxing environments reduce patient anxiety and improve overall safety outcomes.
Selecting qualified providers and verifying their credentials significantly reduces complications from IV therapy for fatigue management.
How Does IV Therapy for Fatigue Compare to Other Energy-Boosting Options?
IV therapy for fatigue compares to other energy-boosting options through differences in absorption rates, speed of effects, and plasma concentration capabilities. The comparison involves evaluating bioavailability, cost factors, and clinical evidence across different delivery methods. The following subsections examine how IV therapy stacks up against oral supplements, analyze cost-value relationships, and identify scenarios where alternative treatments may be preferable.
How Does IV Therapy Stack Up Against Oral Supplements or Energy Drinks?
IV therapy stacks up against oral supplements and energy drinks through superior absorption rates and faster onset of effects. IV vitamins achieve 100% absorption compared to oral vitamins’ 20-50% absorption rate. The intravenous route works almost instantly while oral vitamins require digestive processing.
Oral absorption of vitamin C follows a two-phase, non-linear process with decreasing absorption at higher doses. Increasing oral vitamin C intake produces plasma steady-state concentrations reaching maximum levels of 70-80 µM. IV vitamin C achieves plasma concentrations of 50 mM, representing levels up to 100 times higher than oral maximum.
The bioavailability difference stems from digestive system limitations. Oral supplements face absorption barriers including:
- Gastric acid degradation
- Limited intestinal transporter capacity
- First-pass hepatic metabolism
- Individual digestive variations
Energy drinks provide temporary stimulation through caffeine and sugar without addressing underlying nutrient deficiencies. IV therapy delivers therapeutic nutrient doses directly to cells, bypassing digestive constraints entirely. This comparison reveals why IV therapy produces more comprehensive fatigue relief than oral alternatives.
What Are the Cost Differences and Value Considerations?
The cost differences and value considerations for IV therapy range from $100 to over $500 per session depending on formulation complexity. Basic hydration drips cost $100-$150. Vitamin blends range $150-$250. Specialty treatments reach $250-$500.
The Drip IV Infusion pricing structure includes:
- Value Treatments: $99-$149
- Premium IV Treatments: $199
- Elite IV Treatments: $249
- Ultimate & Signature IV Treatments: $299-$399
Package deals provide significant savings. Premium 5 Pack saves $246. Elite 5 Pack saves $246. Ultimate 5 Pack saves up to $496.
| Treatment Type | Single Session | 5-Pack Savings |
| Premium | $199 | $246 |
| Elite | $249 | $246 |
| Ultimate | $299-$399 | $496 |
The global intravenous hydration therapy market reached USD 2.64 billion in 2024, projected to reach USD 5.66 billion by 2033. North America’s IV hydration therapy market estimated at USD 1.6 billion in 2024 shows 8.7% anticipated CAGR growth. These market dynamics reflect increasing consumer recognition of IV therapy’s value proposition despite higher per-session costs than oral supplements.
When Might Other Treatments Be Preferable to IV Therapy?
Other treatments might be preferable to IV therapy when individuals have normal nutritional intake and no absorption disorders. Limited evidence exists that IV vitamins benefit people with adequate nutrient levels. The purported benefits remain primarily anecdotal or based on self-reported outcomes rather than well-designed randomized clinical trials.
Health insurance rarely covers IV therapy for wellness purposes. This financial barrier makes oral supplementation more accessible for routine nutritional support. Evidence that IV therapy helps healthy people remains anecdotal at best according to clinical reviews.
Oral supplementation suffices for individuals without:
- Malabsorption disorders
- Specific documented deficiencies
- Chronic fatigue conditions
- Post-surgical nutrient requirements
The preference for alternative treatments depends on individual health status, budget constraints, and evidence-based medical necessity. Understanding these comparison factors helps patients make informed decisions about fatigue management strategies aligned with their specific circumstances and health goals.
How Should You Approach IV Therapy for Fatigue With The Drip IV Infusion?
The Drip IV Infusion approaches fatigue treatment through personalized IV therapy protocols that deliver nutrients directly into the bloodstream. IV therapy bypasses digestive limitations to achieve 100% bioavailability, making it particularly effective for individuals experiencing persistent fatigue. The clinic’s specialized formulations combine essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids tailored to each patient’s specific energy needs.
Can The Drip IV Infusion Help With Fatigue Through Personalized IV Treatments?
The Drip IV Infusion helps with fatigue through personalized IV treatments by delivering superior nutrient doses that completely bypass the gastrointestinal system. The Wellness Boost formula combines B-complex vitamins, vitamin C, magnesium, and essential minerals specifically for fatigue and stress management. Athletes benefit from the Performance & Recovery formula containing amino acids, enhanced B vitamins, and specialized recovery compounds. The Revitalize & Rehydrate treatment rapidly restores fluid balance and electrolytes for immediate energy restoration. Direct bloodstream delivery ensures 100% bioavailability compared to oral supplements’ 20-50% absorption rates.
What Are the Key Takeaways About Using IV Therapy to Manage Fatigue?
The key takeaways about using IV therapy to manage fatigue include enhanced energy levels, reduced pain, and improved mental clarity in chronic fatigue patients. The global infusion therapy market reached $11.7 billion in 2023 with 8.6% projected annual growth through 2030. The U.S. mobile IV hydration market valued at $568.25 million in 2024 will reach $1556.29 million by 2034. IV therapy delivers synergistic therapeutic effects uniquely suited to each patient’s clinical profile and wellness goals through customized nutrient combinations.
