If you’re reading this while nursing a pounding headache and queasy stomach after last night’s festivities, you’re likely searching for fast relief from hangover symptoms. We understand the desperation for a quick fix when you’re feeling miserable, and you’ve probably heard about IV therapy as a potential miracle cure. Let’s explore whether this trendy treatment actually delivers on its promises.
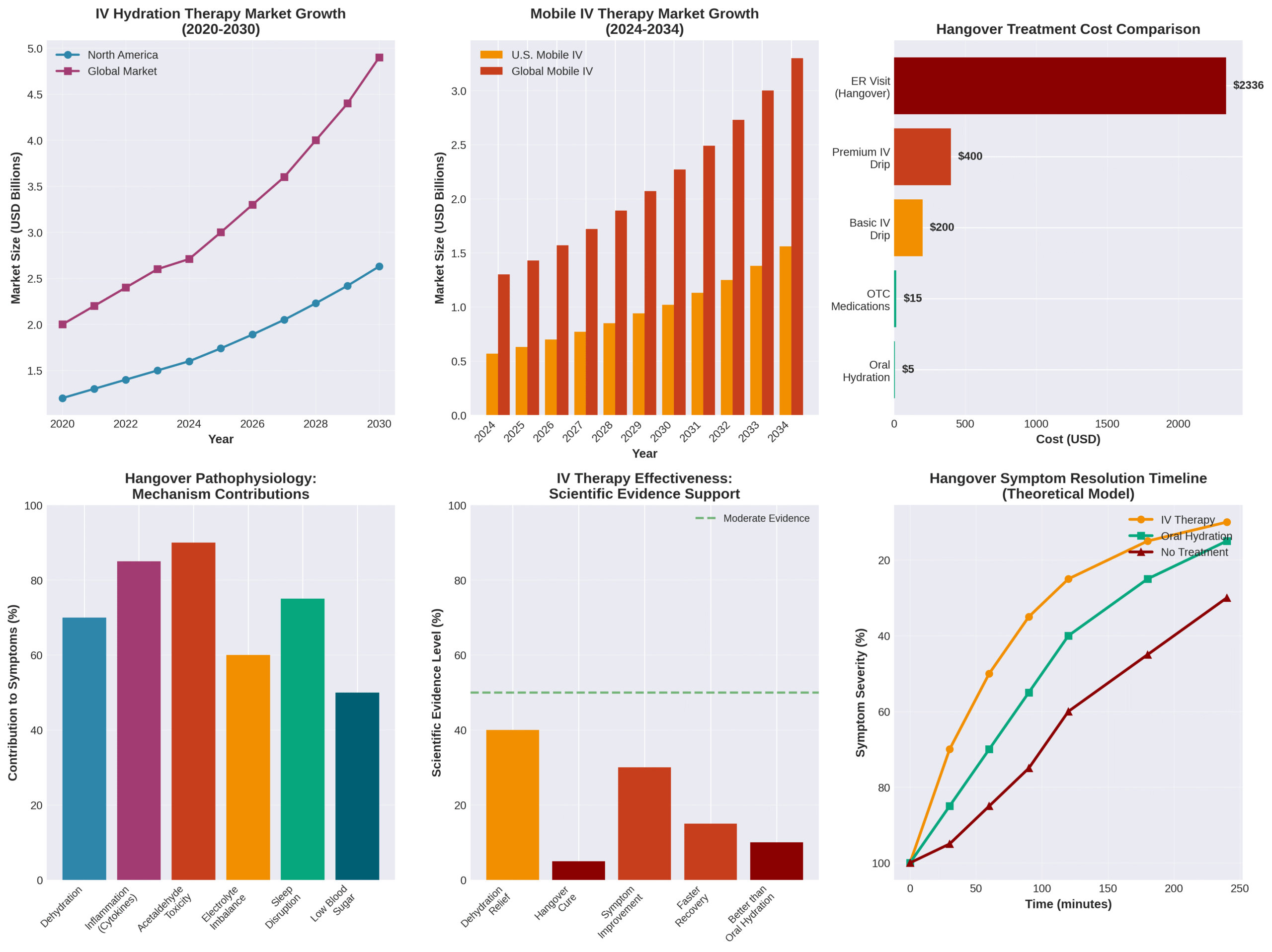
IV therapy for hangovers is a medical treatment that delivers fluids, electrolytes, and vitamins directly into your bloodstream through an intravenous drip, bypassing your digestive system for immediate absorption. While mobile IV therapy services operate 24/7 in over 50 U.S. cities with nurses arriving within 2-6 hours, recent scientific evidence challenges whether this $100-$400 treatment provides meaningful benefits beyond traditional remedies.
According to a 2023 study published in Acute Medicine & Surgery, researchers found that “intravenous fluid did not influence the length of time until awakening in patients with acute alcohol intoxication,” leading them to conclude that “routine use of IVF therapy for acute alcohol intoxication should be avoided.” This finding aligns with mounting evidence that dehydration, while contributing to hangover symptoms, isn’t the primary culprit we once believed it to be.
Dr. Cristina Ignacio, M.D. from Hackensack Meridian Health, explains the limitation clearly: “Rehydrating with IV fluids won’t cure a hangover, because dehydration is only one symptom. An IV treatment – even with added electrolytes or vitamins – can’t address all of the symptoms of hangover, including headache, nausea, trouble concentrating, delayed reaction time or sensitivity to light or loud noises.”
Key takeaways from our comprehensive analysis include:
• IV therapy delivers fluids directly into bloodstream but cannot accelerate alcohol metabolism or address all hangover symptoms
• Scientific studies show no significant difference in recovery time between IV therapy and traditional hydration methods
• Treatment costs range from $100-$400 per session and insurance does not cover hangover IV therapy
• Medical risks include infection at injection site, vein inflammation, blood clots, and electrolyte imbalances
• Healthcare professionals recommend oral hydration, rest, and over-the-counter medications as safer, more cost-effective alternatives
Our investigation reveals a more nuanced picture of hangover recovery. We’ll examine how IV therapy actually works for rehydration, why hangovers occur beyond simple dehydration, and compare IV treatments to traditional remedies. We’ll also discuss who might be a candidate for IV therapy, what to expect during a session, and crucial safety considerations. Most importantly, we’ll help you understand whether The Drip IV Infusion’s services might address your specific recovery needs while providing evidence-based alternatives that your body—and wallet—might prefer.
To help you make an informed decision, here’s one practical tip: Before considering IV therapy, try drinking 16-20 ounces of water with a pinch of salt and a squeeze of lemon juice every hour for three hours—this simple remedy provides hydration and electrolytes at a fraction of the cost and without medical risks.
As we dive deeper into the science and reality of IV hangover treatments, you’ll discover why the best cure might be simpler than you think, and why prevention remains your most powerful tool against future hangover misery.
What Is IV Therapy and How Does It Work for Rehydration?
IV therapy is the delivery of fluids directly into the bloodstream through a vein, bypassing the digestive system for immediate absorption. Standard IV fluids include saline (0.9% sodium chloride in water) or Lactated Ringer’s solution. The treatment takes 45-60 minutes for complete administration. Mobile IV therapy services operate 24/7 in over 50 U.S. cities, with nurses arriving within 2-6 hours of booking.
The following sections explore common ingredients, symptom relief timing, and scientific evidence behind IV therapy for hangovers.
What Ingredients Are Commonly Used in IV Hangover Treatments?
The ingredients commonly used in IV hangover treatments include vitamin complexes, minerals, and saline solutions in specific formulations. Myers’ Cocktail contains 2,500mg Vitamin C, 1mL B-Complex, 5mL Magnesium Chloride (30%), 3mL Calcium Gluconate (10%), 100mg Pyridoxine, 250mg Dexpanthenol, and 1,000mcg Hydroxocobalamin.
The traditional “Banana Bag” includes:
- 1 liter Normal Saline
- 100mg thiamine
- 1mg folic acid
- 1-2g magnesium
- Multivitamin infused over 24 hours
Updated evidence-based formulations recommend 200-500mg IV thiamine every 8 hours instead of the traditional 100mg dose. Hangover-specific IV drips contain Vitamin B Complex, Vitamin C, Glutamine, and 8 trace minerals including Zinc, Iron, Iodine, and Selenium. Calcium dosages range from 200-500mg when given with magnesium to regulate muscle contractions.
How Quickly Can IV Therapy Alleviate Hangover Symptoms?
IV therapy can alleviate hangover symptoms with noticeable improvement typically occurring within 30-45 minutes after administration. Fluids and nutrients bypass the digestive system for faster absorption than oral hydration.
An Australian randomized controlled trial found no difference in emergency department length of stay between the IV fluid group (mean 287 minutes) and non-IV group (mean 274 minutes). A 2023 study on acute alcohol intoxication showed IV fluid did not influence length of time until patient awakening. These findings suggest IV therapy may not provide faster recovery than standard care despite the rapid fluid delivery mechanism.
What Is the Science Behind IV Therapy Effectiveness for Hangovers?
The science behind IV therapy effectiveness for hangovers shows no FDA-approved or clinically-validated studies confirm IV hydration therapy benefits. A 2023 study concluded routine use of IV fluid therapy for acute alcohol intoxication should be avoided. IV fluids cannot accelerate alcohol metabolization based on the mechanism of alcohol metabolism.
Recent research shows no strong link between hangover severity and imbalances in electrolytes, glucose, or hormones. A 2005 systematic review of randomized controlled trials (cited by 160) found limited evidence for hangover treatments. The lack of scientific support indicates IV therapy addresses symptoms rather than underlying hangover mechanisms, making its effectiveness questionable compared to simpler hydration methods.
Why Do Hangovers Occur and What Are Their Main Symptoms?
Hangovers occur when alcohol metabolism produces toxic byproducts while the body processes different types and amounts of alcohol at varying efficiency rates. A 1998 foundational paper by Swift identified multiple mechanisms beyond dehydration that trigger hangover symptoms. A 2021 study evaluated 82 hangover products and found unknown safety and efficacy profiles for most treatments.
The following subsections explore the biological processes, dehydration’s role, and common symptoms that characterize hangovers.
Which Biological Processes Trigger Hangover Symptoms?
The biological processes that trigger hangover symptoms center on toxic byproducts created during alcohol metabolism. The liver processes alcohol at a fixed rate that cannot be accelerated by IV fluids or other interventions. GCS scores provide better indicators of alcohol’s central nervous system effects than hydration status measurements. Higher hemoglobin levels correlate with longer awakening times, suggesting a dehydration connection to recovery duration.
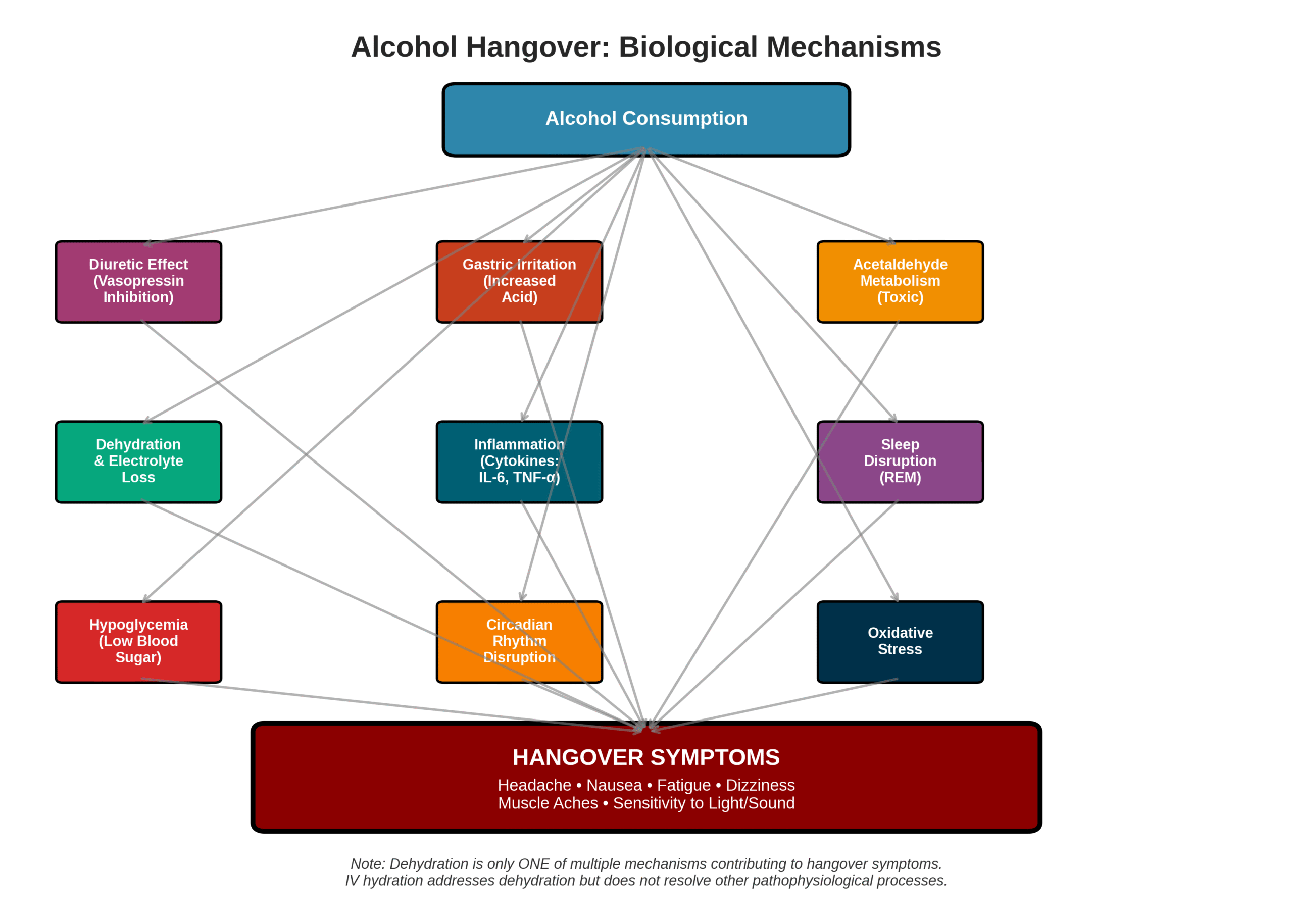
These metabolic processes create cascading effects throughout multiple body systems beyond simple fluid imbalance.
How Does Dehydration Contribute to Hangovers?
Dehydration contributes to hangovers through water and electrolyte loss caused by alcohol’s diuretic effects. A 2024 study demonstrated that dehydration and hangover operate through different mechanisms of action. The popular theory linking dehydration as the primary hangover cause lacks scientific support. Dehydration represents only one symptom among many hangover manifestations.
Understanding dehydration’s limited role helps explain why hydration alone rarely eliminates all hangover symptoms.
What Are the Most Common Signs You Have a Hangover?
The most common signs you have a hangover include headache, nausea, trouble concentrating, and delayed reaction time. Sensitivity to light and loud noises frequently accompanies these primary symptoms. A 2016 study characterized hangover symptoms following intravenous alcohol administration and confirmed fatigue and general malaise as consistent features. Physical symptoms typically combine with cognitive impairment to create the characteristic hangover experience.
These diverse symptoms reflect alcohol’s widespread effects on multiple body systems rather than a single underlying cause like dehydration.
How Does IV Therapy Compare to Traditional Hangover Remedies?
IV therapy for hangovers costs significantly more than traditional remedies while lacking scientific evidence of superior effectiveness. The price difference is substantial—IV treatments range from $100-$400 per session versus a few dollars for over-the-counter remedies. Premium IV treatments containing specialized ingredients can cost $350-$800. Insurance does not cover hangover IV therapy since it’s not medically necessary. A 2023 study showed emergency room Level 4 visit facility fees grew from $1,064 to $2,336 in Colorado, illustrating the high cost of medical-grade IV administration. The following subsections examine effectiveness, risks, and appropriate candidates for each treatment approach.
Is IV Therapy More Effective Than Oral Hydration or Home Cures?
IV therapy is not more effective than oral hydration or home cures for hangover relief. No scientific evidence shows IV drips cure hangovers better than oral hydration. Research demonstrates IV hydration after drinking doesn’t improve hangover symptoms compared to traditional methods. Most people experiencing hangovers can drink the fluids they need without IV therapy. IV drips won’t rehydrate better than drinking fluids in most cases for healthy individuals. Over-the-counter pain relievers work just as well as IV medications for hangover symptoms. The bypass of the digestive system offers faster fluid delivery but doesn’t translate to better hangover resolution since dehydration represents only one component of the complex hangover syndrome.
Are There Risks Associated With Different Hangover Treatments?
Different hangover treatments carry varying risk profiles, with IV therapy presenting more serious potential complications. IV therapy risks include infection at the injection site, vein inflammation, and blood clots. A 2012 study by Dychter (cited by 355) documented IV therapy complications including phlebitis, infiltration, extravasation, and infections. Improperly administered IVs can cause clotting, inflammation, bloodstream infection, and electrolyte imbalance. Potassium overdose from IV therapy can result in potentially fatal arrhythmias. Air embolism can occur when IV administration pushes too much air into a vein. Traditional oral remedies carry minimal risks—primarily limited to potential medication interactions with NSAIDs or excessive water consumption causing hyponatremia.
Who Should Consider IV Therapy Instead of Other Remedies?
The candidates who should consider IV therapy are those with severe dehydration who cannot tolerate oral fluids. Medical professionals reserve IV fluids for people who are dehydrated and unable to take fluids by mouth. Best candidates include individuals with severe nausea or vomiting preventing oral intake. The ability to drink fluids remains the best and safest rehydration method. Traditional remedies work effectively for most hangover sufferers—these include water, chicken broth, NSAIDs like ibuprofen, and rest. IV therapy becomes appropriate only when oral rehydration fails or when medical complications prevent normal fluid consumption. This section establishes that IV therapy serves as a last resort rather than a first-line treatment for hangovers.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Hangover IV Therapy?
Good candidates for hangover IV therapy are people unable to keep fluids down due to severe nausea or vomiting. Those experiencing severe dehydration symptoms requiring immediate intervention may benefit from IV treatment. Individuals must not have contraindications like kidney disease, heart disease, or severe allergies. Healthcare providers should screen patients for medication interactions before administering IV therapy. The following subsections detail medical eligibility, provider discussions, and situations when IV therapy should be avoided.
Are There Medical Conditions That Might Affect Eligibility?
Medical conditions that affect eligibility include kidney disease, heart failure, and liver problems. People with kidney disease should not receive IV therapy unless prescribed by a doctor. Congestive heart failure patients face fluid overload risks from IV administration. Advanced liver problems contraindicate IV therapy due to impaired fluid processing. There are specific genetic conditions, such as G6PD deficiency and hereditary hemochromatosis, that may affect vitamin C and iron metabolism in IV formulations. Heart conditions serve as general contraindications because rapid fluid shifts can strain cardiovascular function.
What Should You Discuss With a Healthcare Provider Before IV Therapy?
You should discuss with a healthcare provider all current medications to check for serious drug interactions. Disclose any history of kidney, heart, or liver disease that could affect IV fluid processing. Previous allergic reactions or severe allergies require careful review, particularly for vitamin and mineral components. Your current health status and chronic conditions determine IV therapy safety parameters. Healthcare providers need to know whether oral hydration has been attempted first, as IV therapy should remain a secondary intervention for those who cannot tolerate oral fluids.
When Should You Avoid IV Therapy for a Hangover?
You should avoid IV therapy for a hangover when you can tolerate oral fluids effectively. Kidney disease, heart disease, or severe allergies make IV therapy unsafe regardless of hangover severity. Medications that interact with IV ingredients, such as diuretics or blood pressure medications, contraindicate treatment. Symptoms unrelated to dehydration like jet lag do not warrant IV intervention. Seeking treatment purely for preventive purposes without medical need exposes you to unnecessary risks including infection, vein inflammation, and electrolyte imbalances.
What Should You Expect During an IV Hangover Therapy Session?
An IV hangover therapy session typically lasts 45-60 minutes for complete fluid administration. Mobile services arrive within 2-6 hours of booking through apps. Licensed nurses or medical professionals administer treatment while patients remain seated or reclined during infusion. Multiple needle attempts may be needed if vein access proves difficult.
The session follows a structured medical protocol despite the non-emergency nature of hangover treatment. Understanding the process, preparation requirements, and potential side effects helps patients make informed decisions about this elective service.
What Is the Process and How Long Does It Take?
The process begins with an initial assessment including vital signs and brief medical history. Nurses place the IV line typically in an arm or hand vein. Standard hangover IV drips complete in 45-60 minutes, though Banana Bag formulations may infuse over 24 hours in clinical settings. Mobile apps allow scheduling and tracking of appointment status throughout the process.
The actual infusion starts once vein access is established. Patients experience immediate fluid entry into their bloodstream. Most report feeling the cooling sensation of fluids within minutes. The complete process from arrival to departure typically takes 60-90 minutes including setup and monitoring.
How Should You Prepare for an IV Therapy Appointment?
Patients should disclose all medications and supplements to their provider before treatment begins. Informing providers of any allergies or previous IV reactions prevents adverse events. Wear comfortable clothing with easy arm access. Stay hydrated before appointment if possible to improve vein visibility. Have medical insurance information ready, though hangover treatment typically lacks coverage.
Preparation also includes mental readiness for the procedure. Some patients experience anxiety about needles. Eating a light meal beforehand prevents lightheadedness. Arrange transportation if feeling significantly impaired. Clear your schedule for at least 90 minutes to avoid rushing through treatment.
Are There Any Side Effects of Hangover IV Therapy?
Common side effects include bruising at the injection site. There is a small chance of infection or blood clot at the injection site. Some patients experience cold sensation during fluid administration. IV therapy may upset electrolyte levels when improperly balanced. Overhydration is possible with excessive fluid administration, particularly in smaller individuals.
Additional reactions vary by individual sensitivity. Mild discomfort during needle insertion affects most patients. Some report metallic taste from certain vitamin infusions. Rare complications include allergic reactions to ingredients. Monitoring by qualified staff reduces these risks significantly during the session.
How Safe and Regulated Is IV Therapy for Hangover Relief?
IV drips for hangovers are not FDA-approved treatments. No clinically-validated studies confirm IV hydration therapy benefits for hangovers. IV therapy follows routine standards in clinical settings but faces less regulation in boutique environments. Six in 10 U.S. adults manage chronic diseases that may contraindicate IV therapy. A 2024 USDA report found foodborne illness causes 3,000 deaths annually with costs exceeding $15.6 billion.
The following subsections examine specific risks, provider qualifications, and safety standards essential for informed decision-making about hangover IV therapy.
What Are the Potential Risks or Side Effects?
Infection is one of the most common complications at IV placement sites. Superficial thrombophlebitis develops when veins become inflamed with blood clots. Bloodstream infections occur with improper administration techniques. Electrolyte imbalances result from inappropriate fluid composition, such as excessive sodium or potassium levels. Air embolism represents a rare but serious complication when IV administration pushes gas bubbles into veins.
A 2012 study by Dychter cited by 355 researchers documented phlebitis, infiltration, and extravasation as primary IV therapy complications. These risks increase outside controlled medical environments where sterile protocols may vary.
How Are IV Therapy Providers Qualified and Regulated?
Clinical settings maintain medical-grade facilities with professional administration protocols. Mobile IV services employ registered nurses but operate with varying oversight levels depending on state regulations. Boutique IV therapy companies function without consistent regulatory standards across jurisdictions. Medical oversight requirements differ significantly by state, creating a patchwork of safety standards. Some services offer ready-to-launch business models with included medical directors who may never physically examine patients.
State nursing boards regulate individual practitioners, but facility standards for non-hospital IV services remain inconsistent. This regulatory gap allows wide variation in safety protocols and medical supervision quality.
What Safety Standards Should You Look For?
Professional medical staff credentials should include registered nurse licensure or higher qualifications. Medical-grade facilities require proper sterilization equipment, emergency supplies, and contamination controls. Clear screening protocols must identify contraindications such as kidney disease, heart conditions, and medication interactions. Emergency protocols and equipment availability indicate preparedness for adverse reactions. Proper documentation systems and active medical director oversight demonstrate accountability standards.
The safest IV therapy providers maintain hospital-level infection control procedures, use single-use sterile equipment, and require physician orders before treatment. These standards help minimize risks associated with IV administration outside traditional healthcare settings.
How Should You Decide If IV Therapy for Hangover Relief Is Right for You?
The decision to use IV therapy for hangover relief depends on whether oral hydration has failed, your specific health conditions, and cost-benefit analysis. Consider that IV therapy costs $100-$400 per treatment without proven superiority over oral remedies. Assess personal contraindications including kidney disease, heart conditions, or severe allergies before treatment. Review alternatives such as rest, oral fluids, and over-the-counter medications that cost significantly less. Consult your healthcare provider if you have underlying medical conditions that could complicate IV therapy administration.
How Can The Drip IV Infusion Address Your Hangover Recovery Needs?
The Drip IV Infusion operates within North America’s IV hydration therapy market, valued at $1.6 billion in 2024. The market projects growth at 8.7% CAGR from 2025 to 2030, reflecting increasing consumer demand. Mobile IV therapy services, including The Drip IV Infusion, contribute to a market expected to reach $1.02 billion by 2030. Global mobile IV hydration services project $2.6 billion valuation by 2030. The Drip IV Infusion integrates technology through app-based booking systems and maintains 24/7 availability for hangover relief services.
What Are the Main Points to Remember About IV Therapy for Hangover?
IV therapy for hangovers addresses dehydration, which represents only one component of hangover symptoms rather than the primary cause. Scientific evidence does not support IV therapy’s superiority over oral remedies for hangover relief. The most effective hangover prevention remains moderate alcohol consumption. IV therapy carries medical risks including infection, vein inflammation, and electrolyte imbalances despite uncommon occurrence rates. Most healthy individuals can achieve effective rehydration through oral fluid consumption without requiring intravenous intervention.
