If you’re curious about Normal Saline because you’ve heard about IV therapy or seen it mentioned when you’re at the doctor’s, you’re in the right place to learn everything about this basic medical solution. We get that you might be thinking about IV therapy or just want to know what’s going into your body during medical treatments. We’ll give you the straight facts you need to make smart choices.
Normal Saline is a clean solution with 0.9% salt water that doctors use more than any other IV fluid around the world. This clear liquid has 9 grams of salt per liter – think of it like the salt content in your tears or sweat. Despite the name making it sound “normal” for your body, that’s actually a mix-up from way back in the 1800s when scientists got it wrong about what matched your blood.
TL;DR Summary:
- Normal Saline has 0.9% salt and is the main IV fluid for when you’re dehydrated, losing blood, or need medicine delivered
- New studies show other IV fluids might be safer for many people, though Normal Saline is still the best choice for brain injuries and certain conditions
- Big amounts of Normal Saline can mess with your body’s acid balance and hurt your kidneys a bit more than other solutions
- It only costs $1-2 to make but hospitals charge $127-700, making it the cheapest IV option
- Doctors now pick IV fluids based on what you specifically need instead of just using Normal Saline for everyone
- The Drip IV Infusion uses Normal Saline as a base for custom IV treatments, mixing its proven safety with extra nutrients
Quick Tip: If you’re getting an IV, ask your provider why they picked Normal Saline over other fluids – the answer should be about your specific health needs, not just because that’s what they always use.
What Are the Main Ingredients and Concentration of Normal Saline?
The main ingredients and concentration of Normal Saline are 0.9 grams of salt per 100 milliliters of water. This sterile solution contains specific amounts of sodium and chloride ions per liter, with a concentration slightly higher than your blood. The acidity level is higher than human blood. Understanding these specifications helps medical professionals and patients recognize why Normal Saline functions as a critical IV fluid in healthcare settings.
How Is Normal Saline Formulated?
Normal Saline is made by dissolving 9 grams of salt in one liter of sterile water. Each liter delivers specific amounts of sodium ions and chloride ions to your bloodstream. The solution maintains a concentration slightly higher than human blood.
Drug manufacturers produce Normal Saline as a clear, colorless, safe solution. The acidity typically measures around a level that’s more acidic than blood’s normal range. Production follows strict drug standards to ensure cleanliness and consistency.
The making process requires precise measurement and mixing under controlled conditions. Quality control tests verify the concentration, cleanliness, and absence of particles before distribution. These manufacturing standards ensure Normal Saline’s reliability as a medical-grade IV solution ready for immediate clinical use.
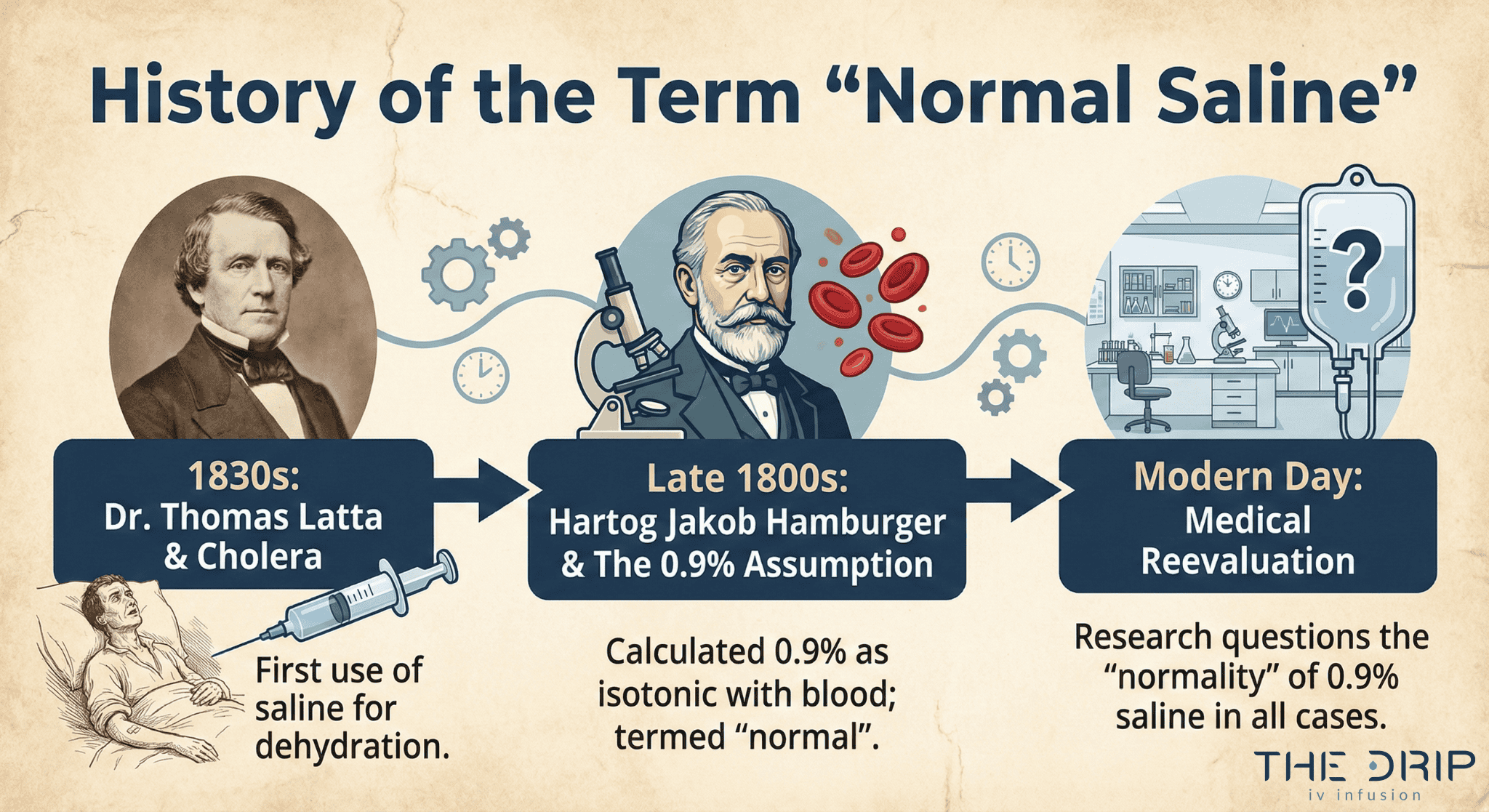
Why Is 0.9% Sodium Chloride Considered “Normal” Saline?
The 0.9% concentration is considered “Normal” Saline due to a historical misunderstanding from the 1800s. Scientists then incorrectly believed this concentration was perfectly balanced with mammalian blood. Dutch scientist Hartog Jakob Hamburger promoted the 0.9% standard in the late 1800s based on incomplete understanding of blood chemistry.
A 2016 study reveals that “the implied normalcy and physiological property have perpetuated indiscriminate use of saline in medical practice.” The term persists despite modern knowledge showing the solution’s chloride content exceeds normal levels. Dr. Thomas Latta first used IV saline during the 1831-1832 European cholera pandemic, establishing its medical foundation.
Today’s medical community recognizes Normal Saline as neither truly “normal” nor perfectly natural for your body. The name endures through medical tradition rather than scientific accuracy. This historical context explains why healthcare providers increasingly evaluate other fluid solutions for specific clinical scenarios where Normal Saline’s makeup may not be optimal.
How Is Normal Saline Used in Medical and Wellness Settings?
Normal Saline serves critical roles across medical and wellness applications. Healthcare providers use this 0.9% salt solution for fluid replacement, medicine delivery, and surgical support in diverse clinical scenarios.
In What Medical Situations Is Normal Saline Administered?
Medical situations for Normal Saline use include approved uses for replacing lost body fluid in dehydration, low blood volume, bleeding, and serious infections. The solution treats certain chemical imbalances when fluid loss occurs and manages mild sodium loss effectively.
Healthcare facilities use Normal Saline as a priming solution for kidney dialysis procedures. Medical teams use it to start and end blood transfusions safely. The solution works as a medicine mixer for compatible drug additives, enabling precise medication delivery.
Surgical teams apply Normal Saline as a washing solution during procedures to keep tissue moist and clear surgical fields. Emergency departments give it for acute adrenal problems, where rapid sodium replacement proves essential.
What Role Does Normal Saline Play in IV Therapy?
The role of Normal Saline in IV therapy centers on expanding blood volume through sodium and chloride ions. These primary chemicals of body fluid restore blood volume and maintain cell function.
Over 200 million liters of Normal Saline are used annually in the United States alone. The solution serves as the most widely used IV fluid in clinical practice worldwide. Healthcare providers rely on it as a vehicle for medicine delivery when working as a drug mixer.
Normal Saline enables rapid blood vessel access for emergency interventions. Medical teams select it for initial treatment before lab results become available.
How Is Normal Saline Used in Dehydration and Fluid Replacement?
Normal Saline is used in dehydration and fluid replacement by quickly restoring blood volume and correcting salt and water losses. The solution replaces lost fluids through vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive sweating.
Medical guidelines emphasize early, aggressive fluid replacement, though recent evidence favors more careful use. Clinical protocols now recommend careful volume assessment to prevent fluid overload complications.
Stomach doctors recommend against Normal Saline for acute pancreas inflammation, citing acid balance risk. Healthcare providers monitor acid-base balance during high-volume infusions to detect early signs of acid problems.
This widespread medical application of Normal Saline demonstrates its fundamental importance in healthcare delivery, though evolving evidence guides more selective use based on specific patient conditions.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Normal Saline?
Normal Saline offers distinct advantages and limitations that guide clinical decision-making in IV therapy. Healthcare providers weigh these factors when selecting fluids for specific patient needs.
What Are the Primary Advantages of Using Normal Saline?
Normal Saline provides several advantages in specific clinical scenarios where fluid balance is critical. These strengths make it one of the most frequently used solutions worldwide.
Key advantages include:
- Safety for brain injury patients
- Effective potassium reduction
- Extremely low manufacturing cost
- Simple single-chemical formulation
- Broad medication and blood product compatibility
Are There Risks or Side Effects Associated with Normal Saline?
Yes. Normal Saline carries risks such as acid–base disturbances, kidney injury, fluid overload, and incompatibility with certain medicinesLarge-volume infusions cause acid balance problems due to high chloride concentration compared to what’s normally in your blood.
The SMART trial found Normal Saline associated with higher acute kidney injury rates compared to other fluids. Patients with heart or kidney problems face increased fluid overload risk. Normal Saline proves incompatible with certain medicines.
Situations where Normal Saline can’t be used include:
- Significantly high sodium
- High chloride
- Significant fluid overload
- Severe heart failure
- Advanced kidney disease
When Might Alternative IV Solutions Be Preferred Over Normal Saline?
Other IV solutions are preferred over Normal Saline in serious infections, diabetic emergencies, pancreas inflammation, and severe liver disease. The SMART trial analysis showed other fluids reduced 30-day hospital deaths in infection patients compared to saline.Stomach doctors recommend other solutions over Normal Saline for pancreas inflammation.Choosing the right IV fluid depends on the clinical condition, acid–base effects, and metabolic capacity. The following table summarizes when alternatives outperform Normal Saline.
| Clinical Scenario | Preferred Solution | Rationale |
| Sepsis | Balanced crystalloids | Lower mortality (SMART trial) |
| Diabetic ketoacidosis | Balanced crystalloids | Faster resolution |
| Acute pancreatitis | Lactated Ringer’s | Reduced metabolic acidosis risk |
| Severe liver disease | Normal Saline | Avoids lactate accumulation |
Patients with severe liver disease benefit from Normal Saline over Lactated Ringer’s due to reduced lactate metabolism capacity. These clinical nuances inform individualized fluid selection strategies.
How Does Normal Saline Compare to Other IV Fluids?
Normal Saline compares to other IV fluids through distinct chemical makeups, acid levels, and clinical applications. The primary differences center on sodium and chloride concentrations versus balanced solutions containing additional chemicals. Understanding these comparisons helps medical providers select optimal fluid therapy based on patient conditions and treatment goals.
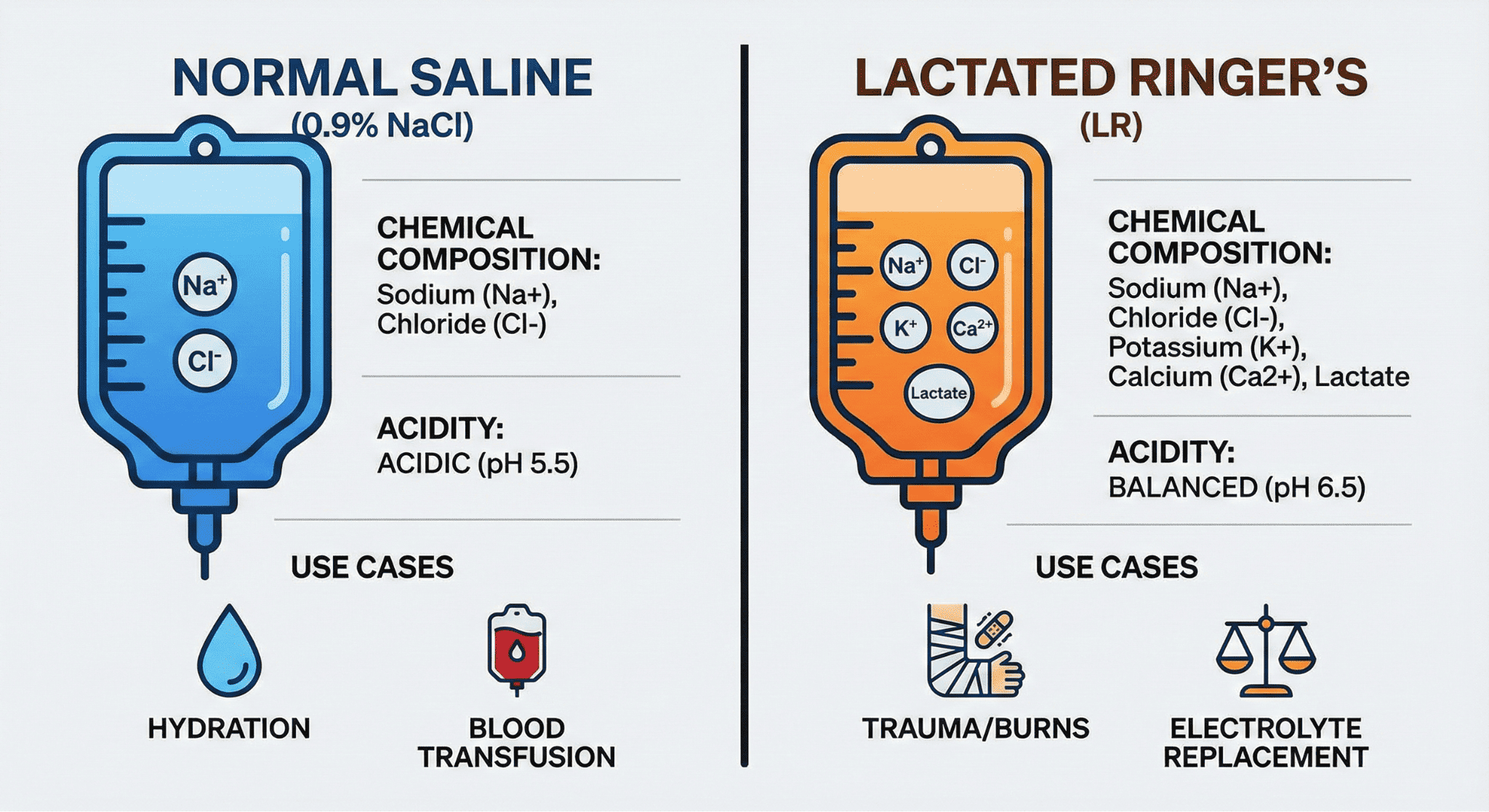
What Are the Key Differences Between Normal Saline and Lactated Ringer’s?
The key differences between Normal Saline and Lactated Ringer’s are found in their sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, and lactate content. Normal Saline contains equal amounts of sodium and chloride, while Lactated Ringer’s contains less sodium and chloride.
Lactated Ringer’s includes additional chemicals absent in Normal Saline:
• Potassium
• Calcium
• Lactate (turned into bicarbonate by your liver)
These makeup differences influence fluid distribution and body effects, making each solution suited for specific clinical scenarios.Normal Saline and Lactated Ringer’s differ significantly in electrolyte composition and physiologic effects. The table below highlights the main distinctions.
| Solution | Sodium | Chloride | Additional Components | Acidity |
| Normal Saline | High | High | None | More acidic |
| Lactated Ringer’s | Moderate | Moderate | Potassium, Calcium, Lactate | Less acidic |
Why Might a Medical Provider Choose Normal Saline Over Other Solutions?
A medical provider may choose Normal Saline over other solutions because it is safer for brain injury, better tolerated in liver disease, and more cost-effective. The BaSICS trial found higher death rates in brain injury patients treated with balanced solutions, reinforcing Normal Saline use for brain injury cases.
Normal Saline is preferred in liver disease patients because liver dysfunction may mess up chemical processing from other solutions, potentially raising chemical levels. Money considerations also influence selection – other fluids cost 2 to 4.5 times more than Normal Saline at wholesale level, creating pressure favoring Normal Saline use.
A 2025 major hospital study involving 43,000 patients found no significant difference in death or readmission between different fluid policies. This finding suggests both fluids provide comparable outcomes in general hospital populations.
These comparisons demonstrate that Normal Saline remains valuable for specific conditions despite the availability of other alternatives, with selection depending on individual patient factors and hospital protocols.
What Should Patients Know Before Receiving Normal Saline?
Normal saline administration requires careful patient assessment and monitoring. Healthcare providers evaluate specific medical conditions, situations where it can’t be used, and expected outcomes before starting therapy. Understanding who’s a good candidate, precautions, and infusion procedures helps patients make informed decisions about their treatment.
Who Is a Candidate for Normal Saline Infusion?
Candidates for Normal Saline infusion are patients who require rapid fluid replacement, sodium correction, dialysis priming, or brain-injury-appropriate fluids. There are four primary indications: volume loss states such as dehydration and low blood volume, chemical imbalances including certain alkaline conditions, procedural requirements for dialysis priming, and brain conditions like traumatic brain injury.
Patients experiencing significant blood loss benefit from normal saline’s rapid volume expansion properties. Those with mild sodium loss receive targeted chemical replacement through the solution’s sodium content. Healthcare providers select normal saline for brain-injured patients because proper fluids prevent brain swelling from worsening.
The following sections detail specific precautions and monitoring requirements for these patient populations.
What Precautions or Contraindications Exist for Normal Saline?
Clinicians must screen patients for conditions that worsen with excess sodium or chloride.
Normal Saline should NOT be used in patients with:
☐ High sodium
☐ High chloride
☐ Lung fluid buildup
☐ Significant fluid overload
☐ Sodium-sensitive cardiac or renal conditions
Monitoring protocols help identify complications early during treatment.
What Can Patients Expect During a Normal Saline Infusion?
Patients can expect close monitoring of urine output, swelling, vital signs, and lab values during a Normal Saline infusion. Healthcare teams track urine output targeting above specific levels and assess for swelling development. Lab monitoring includes blood chemicals, bicarbonate, kidney function tests, and blood gases.
Critically ill patients receive advanced monitoring through central line pressure measurements and heart ultrasound assessments. Despite production costs of $1-2 per liter, hospital charges range from $127 to over $700 per bag.
A team coordinates care delivery. Doctors prescribe appropriate volumes, nurses monitor vital signs and infusion rates, and pharmacists verify medicine compatibility. This team approach ensures safe administration while detecting adverse effects promptly.
Understanding these aspects of normal saline therapy prepares patients for their treatment experience and promotes informed participation in care decisions.
How Can You Safely Experience the Benefits of Normal Saline IV Therapy with The Drip IV Infusion?
Normal Saline IV therapy offers rapid hydration and chemical balance when given by qualified professionals. The Drip IV Infusion ensures safe delivery through medical oversight, clean protocols, and personalized treatment plans tailored to individual wellness needs.
How Does The Drip IV Infusion Incorporate Normal Saline in Its Services?
The Drip IV Infusion incorporates Normal Saline as the foundation of its customized IV therapy treatments. Each infusion begins with drug-grade 0.9% salt solution meeting strict cleanliness standards. Licensed medical professionals assess hydration status before determining appropriate volume and infusion rate.
The Drip IV Infusion combines Normal Saline with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants based on specific wellness goals. Treatment options include hydration therapy, athletic recovery, immune support, and energy enhancement formulas. Mobile service brings treatments directly to homes, offices, or hotels for convenience.
Medical screening protocols ensure safety before each infusion. Nurses monitor vital signs throughout treatment and adjust flow rates as needed. The Drip IV Infusion maintains emergency protocols and supplies for immediate response to any bad reactions.
What Are the Key Takeaways About What Is Normal Saline?
The key takeaways about Normal Saline are that it is a 0.9% salt solution with proven safety, specific advantages, and growing competition from alternative fluids. Normal Saline contains 0.9% salt, providing specific amounts of sodium and chloride ions per liter. This solution expands blood volume without causing harmful fluid shifts.
A 2025 major trial involving 43,000 patients found no significant death difference between Normal Saline and other fluids in general hospital populations. The BaSICS trial confirmed Normal Saline superiority for brain injury patients. Manufacturing costs remain low at $1-2 per liter, though hospital charges range from $127-700.
Recent evidence supports individualized fluid selection rather than universal protocols. The SMART trial showed other fluids reduced kidney injury rates compared to Normal Saline. Medical experts advocate careful clinical reasoning when selecting IV fluids based on patient-specific factors.
The Drip IV Infusion applies this evidence-based approach through comprehensive assessment and customized treatment protocols, ensuring clients receive appropriate IV therapy aligned with current medical guidelines and individual wellness objectives.