If you’re dealing with awful morning sickness, feeling dried out like a raisin, or your body’s missing key nutrients during pregnancy, you might wonder if IV therapy could give you some relief. We get it – pregnancy throws your body some real curveballs, and you want to be super careful about any treatment while you’re growing your little one. You’ve come to the right spot to learn whether IV therapy is safe for you and your baby.
Here’s what IV therapy during pregnancy really means: doctors give you fluids, nutrients, and safe medications straight into your vein to help with specific pregnancy problems like severe dehydration from throwing up constantly, not having enough iron in your blood, or missing important nutrients. Whether it’s safe depends on having the right doctor watching over you, good reasons for doing it, and knowing what’s okay at different stages of your pregnancy.
TL;DR Summary: IV therapy basically puts fluids and nutrients straight into your bloodstream, and pregnancy changes how your body handles this stuff because your heart pumps 30-50% harder and your blood volume goes up by 40-50%. Doctors commonly use it for severe morning sickness that hits up to 3% of pregnant women and iron-poor blood that affects 37% of women worldwide – a 2025 study showed IV iron works way better than pills. The good news? You get quick relief and your stomach doesn’t get upset like with oral treatments. But there are downsides too: you might get too much fluid, mess up your salt levels, or have problems where the needle goes in, so you absolutely need a doctor’s okay. Safety changes depending on how far along you are – the first few months when your baby’s organs are forming need extra care, while later in pregnancy doctors might give you IV iron if you really need it. When done right with proper medical watching, IV therapy can safely help with specific pregnancy problems, but randomly getting IV fluids without good reason could hurt both you and your baby.
Quick Tip: Always make sure any IV therapy place uses special pregnancy protocols and gets your baby doctor’s thumbs up before treatment – don’t assume that regular IV mixtures are automatically okay when you’re expecting.
As we dig into the science behind IV therapy during pregnancy, you’ll learn how your changing body affects treatment safety, which problems benefit most from IV treatment, and what questions to ask your medical team when thinking about this option. The sections ahead will walk you through research-based info to help you make smart choices about IV therapy while keeping both you and your baby safe and healthy.
What Is IV Therapy and How Does It Work During Pregnancy?
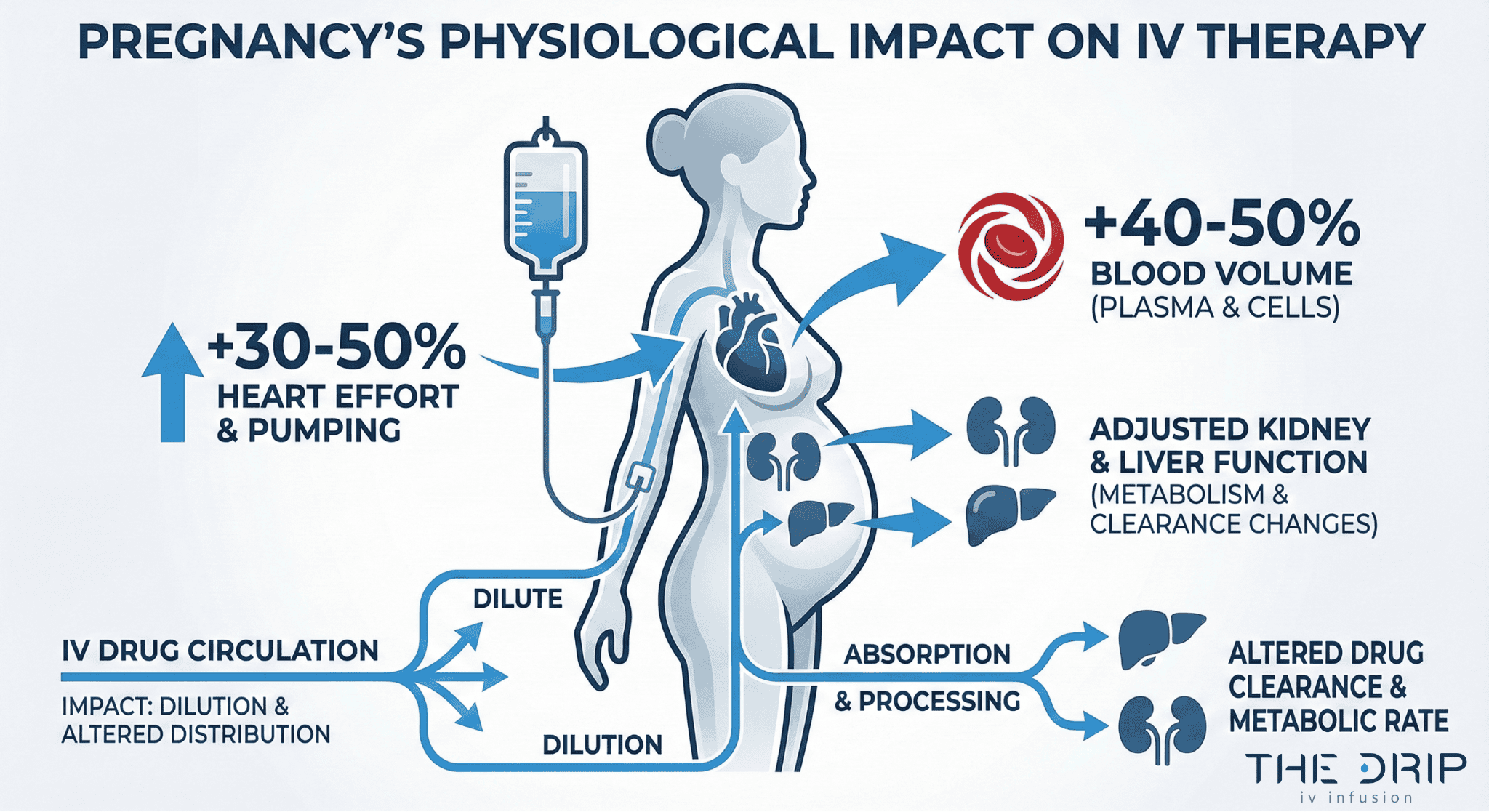
IV therapy works during pregnancy by delivering fluids, medications, and nutrients directly into your bloodstream while accounting for major cardiovascular and metabolic changes. Pregnancy totally changes how your body handles IV treatments because everything inside you is working overtime. Your heart pumps 30-50% harder while your blood volume shoots up by 40-50%. These changes happen fast – 75% of that heart pump increase happens by the end of your first three months.
Your blood vessels relax during pregnancy, kind of like loosening a tight belt. Your blood pressure hits its lowest point around 20-24 weeks. The protein in your blood gets watered down, making you look anemic even when you might not be. Your kidneys work faster too, which means medications get flushed out quicker and doctors often need to adjust IV doses.
These body changes affect how well IV therapy works and how safe it is throughout your pregnancy. Let’s look at what kinds of IV therapy pregnant women commonly get, how it’s different from taking pills or drinks, and when doctors say you need it.
What Types of IV Therapy Are Commonly Used for Pregnant Women?
The main types of IV therapy for pregnant women are fluid replacement, iron treatments, and vitamin cocktails. IV fluids help when you can’t keep anything down because of severe morning sickness, which hits 0.3-3% of pregnancies hard. Iron shots like ferric carboxymaltose fix the low iron that affects 37% of pregnant women around the world.
Medical-grade IV solutions packed with vitamins and nutrients quickly fix what your body’s missing. Each type tackles specific pregnancy problems by going straight into your bloodstream.

How Does IV Therapy Differ From Oral Hydration or Supplementation?
IV therapy and oral supplementation differ in several measurable ways that influence treatment decisions during pregnancy. The table highlights clinically relevant differences in absorption, effectiveness, and maternal–infant outcomes.
| Treatment Type | Attribute | Value |
| IV iron | Anemia correction rate | Higher than oral iron |
| IV iron | GI side effects | Significantly fewer |
| Oral iron | Birthweight outcome | Lower than IV iron group |
| IV iron | Absorption | 100% bloodstream delivery |
| Oral hydration | Labor guidance | Recommended over routine IV by ACOG |
When Might a Doctor Recommend IV Therapy in Pregnancy?
Doctors recommend IV therapy for specific pregnancy-related medical needs. These indications help guide safe and appropriate use.
Common reasons include:
- Severe dehydration from persistent nausea and vomiting
- Iron deficiency anemia unresponsive to oral iron
- Nutrient deficiencies late in pregnancy
- Hospitalization for severe morning sickness
- Intolerance to oral supplements
Knowing when IV therapy becomes necessary helps pregnant women and their doctors make smart treatment choices about staying hydrated and getting proper nutrition.
What Are the Potential Benefits of IV Therapy for Pregnant Women?
The potential benefits of IV therapy for pregnant women include rapid hydration, effective anemia treatment, and fast nutrient delivery when oral intake fails. IV therapy gives crucial support for problems like severe morning sickness and iron deficiency that can mess with both mom’s and baby’s health during pregnancy.
Can IV Fluids Help With Morning Sickness or Dehydration?
Yes. IV fluids can help with morning sickness or dehydration by restoring hydration quickly when you cannot keep anything down. A 2024 study on outpatient IV therapy for severe morning sickness found it worked just as well as being in the hospital while cutting down on how long you’d need to stay there. Severe morning sickness affects 0.3-3% of pregnant women, causing such bad nausea and vomiting that dangerous dehydration sets in and needs medical help.
IV therapy delivers salt water solutions right into your bloodstream, skipping your upset stomach completely. This direct line to your veins gets your fluid levels back to normal in hours instead of days, preventing scary complications like messed up salt levels, weight loss, and dangerous substances showing up in your pee.
Are There Nutrients or Vitamins in IV Therapy That Support Pregnancy Health?
The nutrients or vitamins in IV therapy that support pregnancy health include iron compounds, B vitamins, and essential minerals formulated for pregnancy needs. According to a 2025 study of 3,842 pregnant women, IV iron therapy fixed iron deficiency anemia way better than taking iron pills, and 37% of pregnant women worldwide deal with this problem. Babies whose moms got IV iron showed higher average birth weights compared to those whose moms took iron pills. IV mixtures deliver iron compounds like ferric carboxymaltose or iron sucrose straight into your blood circulation, reaching levels you just can’t get from swallowing pills.
| Nutrient | Clinical Role in Pregnancy | Measured Outcome | Source/Year |
| IV Iron | Anemia Correction Rate | Superior to oral | Meta-analysis 2025 |
| Pregnancy Anemia | Global Prevalence | 37% | WHO 2025 |
| Infant Birthweight | IV vs Oral Iron | Higher with IV | Clinical Trial 2025 |
| Iron Absorption | Bioavailability | 100% venous | Pharmacology 2024 |
How Quickly Do Pregnant Women Experience Relief From IV Treatments?
Pregnant women experience relief from IV treatments within 15–60 minutes for hydration issues and within 24–48 hours for anemia symptoms. A 2025 study showed IV therapy gives faster anemia relief compared to oral supplements, which take weeks to show improvement. Going straight into your veins skips your digestive system entirely, so fluids and nutrients hit your bloodstream immediately at the right concentrations.
Dehydration symptoms like feeling dizzy, tired, and sick to your stomach get better as your blood volume gets back to normal during the treatment session. Iron deficiency symptoms like weakness and trouble breathing improve within days as your blood iron levels climb up. The speed of relief makes IV therapy especially valuable for late-pregnancy situations where time is running out before delivery.
What Are the Risks or Side Effects of IV Therapy During Pregnancy?
The risks or side effects of IV therapy during pregnancy include injection-site complications, fluid overload, electrolyte imbalances, and potential maternal–infant effects. Understanding these risks helps pregnant women make smart decisions about IV therapy.
What Are Possible Short-Term Side Effects for Pregnant Women?
Short-term side effects require careful monitoring to prevent escalation during pregnancy.
These may include:
- Pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site
- Fluid overload from excessive administration
- Electrolyte imbalances such as low sodium
- Newborn complications like respiratory distress
- Infection risks
Are There Any Long-Term Risks to the Mother or the Baby?
Yes. There are potential long-term risks to the mother or baby, primarily from excessive IV fluid causing electrolyte disturbances and downstream complications. When mom’s salt levels drop too low, the baby gets too much fluid, leading to greater newborn weight loss and delayed milk production.
A 2023 review found no solid guidelines specifically for checking hydration during labor, showing big gaps in long-term outcome information. Not having standardized rules increases the chance for unrecognized complications affecting mom and baby health outcomes.
Which Ingredients in IV Therapy Should Pregnant Women Avoid?
The IV therapy ingredients pregnant women should avoid depend on trimester-specific safety data and FDA Pregnancy and Lactation Labeling Rule (PLLR) evaluations. The first three months are a critical time when the baby’s organs are forming and the developing baby is particularly vulnerable to harmful drug effects.
The FDA’s Pregnancy and Lactation Labeling Rule (PLLR) replaced letter grades with detailed descriptions providing specific medication safety information. Healthcare providers must check each IV therapy ingredient against current safety data to protect both mom’s and baby’s health during this vulnerable time.
Who Determines If IV Therapy Is Appropriate During Pregnancy?
An OB-GYN or qualified healthcare provider determines if IV therapy is appropriate during pregnancy through careful medical evaluation. Healthcare providers look at multiple things including mom’s health status, baby’s wellbeing, and specific medical reasons before recommending IV treatment.
What Role Does an OB-GYN or Healthcare Provider Play in This Decision?
An OB-GYN or healthcare provider plays the role of evaluating physiological changes, medication effects, and safety guidelines before approving IV therapy. These changes include a 30-50% increase in how hard your heart pumps and 40-50% expansion in your blood volume that change how medications work in your body.
The FDA’s new Pregnancy and Lactation Labeling Rule (PLLR) helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about using medications during pregnancy. This format replaces the old letter grades with descriptive safety information tailored to different pregnancy stages.
Trained medical professionals should give IV therapy to pregnant women according to established protocols from reputable providers. OB-GYNs evaluate individual patient needs against potential risks before giving the green light for treatment.
Are There Certain Medical Conditions Where IV Therapy Is Unsafe in Pregnancy?
Yes. Certain medical conditions such as serious kidney disease and heart problems can make IV therapy unsafe during pregnancy. These conditions affect how your body processes fluids and keeps your heart stable, potentially making IV treatment dangerous.
Women with these conditions need specialized evaluation before considering IV therapy. The check-up includes kidney function tests, heart monitoring, and consultation with high-risk pregnancy specialists when necessary.
Other conditions that might rule out IV therapy include severe preeclampsia with fluid restrictions, certain autoimmune conditions, and active infections at potential IV sites. Each case needs its own individual risk-versus-benefit analysis.
What Informed Consent or Precautions Should Be Taken Before Treatment?
The informed consent steps or precautions needed before IV therapy in pregnancy include reviewing FDA labeling elements, risk summaries, and clinical considerations. Healthcare providers must discuss these elements with patients before starting IV therapy.
The PLLR format addresses pregnancy testing, birth control, and fertility considerations for women of reproductive age. This comprehensive approach makes sure patients understand both immediate and potential long-term implications of IV treatment.
Precautions include baseline lab work, checking vital signs, and setting up emergency protocols for bad reactions. Writing down mom’s medical history, current medications, and allergies forms essential parts of the consent process.
The upcoming sections will explore how IV therapy safety recommendations change by trimester, looking at specific considerations for each stage of pregnancy.
How Do Safety Recommendations for IV Therapy Vary by Trimester?
Safety recommendations for IV therapy vary by trimester because each stage has different developmental risks and medication-processing changes. The first trimester’s organ-forming period makes developing babies particularly vulnerable to harmful drug effects. UK guidelines recommend thinking about IV iron from the second trimester onwards for iron deficiency anemia.
Blood volume expansion peaks at 32 weeks gestation, affecting third-trimester IV medication concentrations. The following sections look at trimester-specific safety considerations and changing pregnancy needs.
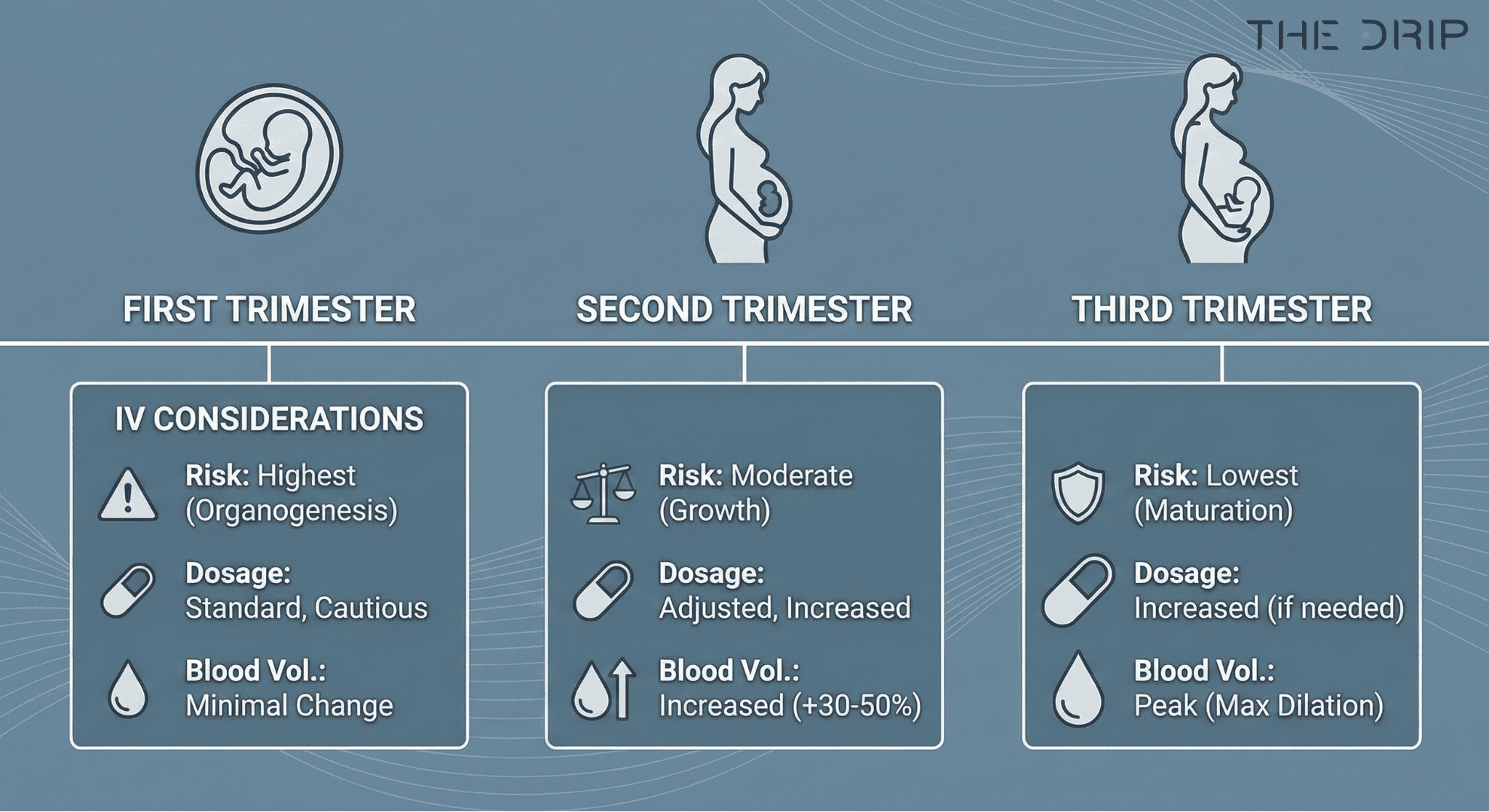
Is IV Therapy Safe During the First, Second, or Third Trimester?
Yes. IV therapy can be safe during the first, second, and third trimesters when administered appropriately under medical supervision, though precautions differ for each stage. The first trimester’s organ formation makes developing babies vulnerable to harmful effects. UK guidelines recommend IV iron starting from the second trimester for safety. Blood volume peaks at 32 weeks, watering down third-trimester medications. Heart output increases 75% by the first trimester’s end, affecting drug distribution right away.
| Pregnancy Stage | Key Factor | Effect |
| First trimester | Organogenesis | Highest vulnerability to drug effects |
| Second trimester | IV iron initiation | Recommended start per UK guidelines |
| Third trimester | Blood volume peak | 32 weeks |
| First trimester | Cardiac output increase | 75% of total increase occurs |
Healthcare providers adjust protocols based on these trimester-specific changes to ensure both mom and baby stay safe throughout pregnancy.
How Might the Needs or Risks Change as Pregnancy Progresses?
As pregnancy progresses, your body undergoes metabolic and circulatory changes that affect IV therapy safety and dosing.
Progression-related factors include:
- Increasing kidney filtration requiring dose adjustments
- Late pregnancy anemia requiring urgent IV iron after 34 weeks
- Changing liver enzyme activity altering drug clearance
- Shifts in blood volume affecting medication concentration
These body adaptations require continuous monitoring and treatment modifications as pregnancy advances toward delivery.
What Are the Alternatives to IV Therapy for Pregnant Women?
The alternatives to IV therapy for pregnant women include oral supplements, dietary changes, and selective hospitalization depending on symptom severity. A 2025 study comparing 3,842 pregnant women found oral iron remains the go-to treatment for iron deficiency anemia despite IV iron working better. ACOG backs drinking fluids over routine continuous IV drips for labor that’s progressing naturally.
Are Oral Supplements or Dietary Changes Effective for Managing Symptoms?
Yes. Oral supplements and dietary changes can be effective for managing symptoms in many pregnant women. Iron pills remain the first-choice treatment for iron deficiency anemia according to current guidelines, though the 2025 study showed IV iron achieves higher blood iron levels. ACOG supports drinking fluids as an alternative to routine continuous IV drips for women in naturally progressing labor. The WHO doesn’t recommend IV fluids for shortening labor time, backing up the validity of non-IV alternatives.
Dietary iron sources include lean meats, leafy greens, and fortified cereals. Vitamin C helps iron absorption when eaten at the same time. Oral rehydration solutions containing electrolytes can effectively manage mild dehydration. These alternatives avoid injection site reactions and infection risks that come with IV therapy while letting patients keep up their normal activities.
When Might Hospitalization Be Preferred Over Outpatient IV Therapy?
Hospitalization may be preferred over outpatient IV therapy during pregnancy when severe complications require continuous monitoring. Severe morning sickness remains a leading cause of hospitalization in early pregnancy, affecting 0.3-3% of pregnancies despite outpatient IV therapy being available. Studies show outpatient IV therapy can match hospital treatment effectiveness for severe morning sickness, potentially avoiding hospitalization costs and disruption.
Hospitalization becomes necessary when patients have severe salt imbalances, can’t stop throwing up long enough to drink anything, or show signs of baby distress. Hospital care provides 24-hour monitoring, immediate intervention capabilities, and access to a whole medical team. The decision between outpatient and hospital treatment depends on symptom severity, home support systems, and how close you live to medical facilities. Understanding these alternatives helps pregnant women and healthcare providers pick the most appropriate treatment setting for the best mom and baby outcomes.
How Should You Evaluate IV Therapy Options During Pregnancy With The Drip IV Infusion?
You should evaluate IV therapy options during pregnancy with The Drip IV Infusion by reviewing provider qualifications, safety protocols, and medical oversight.. The Drip IV Infusion offers specialized IV therapy services for pregnant women, emphasizing medical-grade solutions and professional administration. Understanding their approach alongside general safety guidelines helps expecting mothers make informed treatment decisions.
Can The Drip IV Infusion Safely Support Pregnant Women With IV Therapy?
Yes. The Drip IV Infusion states that they can safely support pregnant women with IV therapy by using medical-grade fluids administered by trained professionals. Their services include IV therapy for better hydration, quick nutritional deficiency correction, and severe pregnancy symptom relief. The company emphasizes professional medical oversight throughout the treatment process. Specific protocol details, IV solution ingredients, and treated conditions aren’t publicly available on their website. Prospective patients should ask for detailed information about pregnancy-specific protocols, staff qualifications, and safety measures during consultation. The absence of published treatment specifics means you need to talk directly with their medical team before moving forward.
What Are the Key Takeaways About the Safety of IV Therapy During Pregnancy?
The key takeaways about the safety of IV therapy during pregnancy are that it can be safe when medically indicated, carefully monitored, and adapted to trimester-specific needs. When properly supervised, IV therapy during pregnancy supports issues like dehydration and anemia while avoiding risks such as fluid overload or electrolyte imbalance. Always work closely with a qualified OB-GYN to determine whether IV therapy during pregnancy is the right choice for your health and your baby’s wellbeing.