Intravenous (IV) therapy has become one of the most revolutionary treatments in the modern medical world. They allow fast, effective, and painless fluid administration of crucial medication, vitamins, and nutrients directly into a patient’s bloodstream. However, if you’re getting an IV treatment, you might wonder why the nurse placed your IV in a specific spot. So, what are the primary IV sites on forearm?
The forearm is one of the most common sites for IV treatments due to its accessibility, flexibility, and ease of use. Selecting the right IV insertion site in the forearm is a critical decision nurses face each day. With the help of professional medical teams in the best mobile IV drip AZ, you can confidently indulge in the benefits of IV therapy.
In this article, we’ll explore why the forearm is a suitable insertion site and what types of medications or fluids can be administered through a forearm IV. You’ll also learn everything you need to know about the primary IV insertion sites on forearm and their advantages.
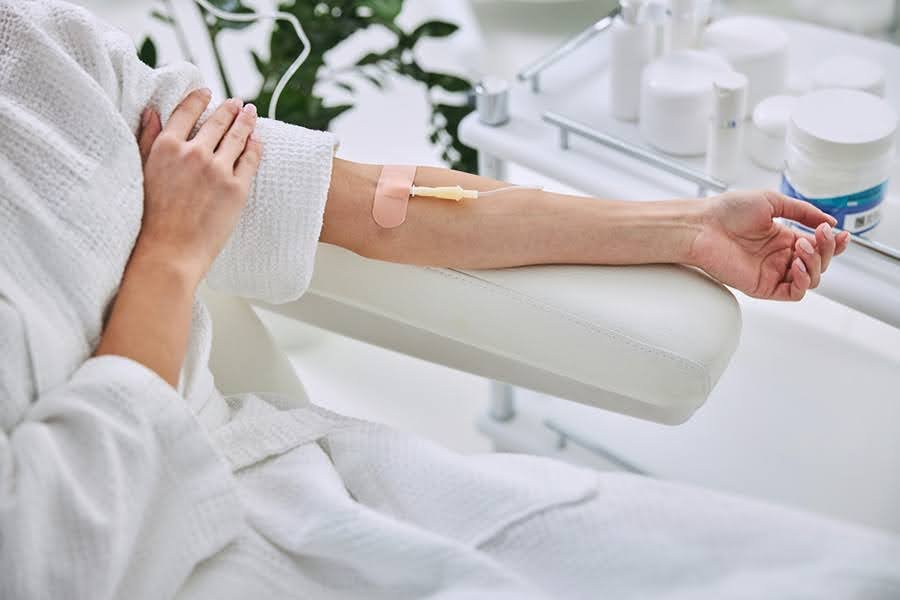

Source: shutterstock.com / Photo Contributor: YAKOBCHUK VIACHESLAV
IV Sites on Forearm
What are the best IV sites in the forearm? When it comes to IV insertions, the forearm is a preferred option among medical professionals as the veins in the forearm are easier to locate.
So, when choosing which site to insert the IV drip in, medical professionals need to go through the patient’s treatment requirements, medical condition, and age. Additionally, the vein condition, patient comfort, and potential complications all play a role in selecting the most suitable forearm IV site.
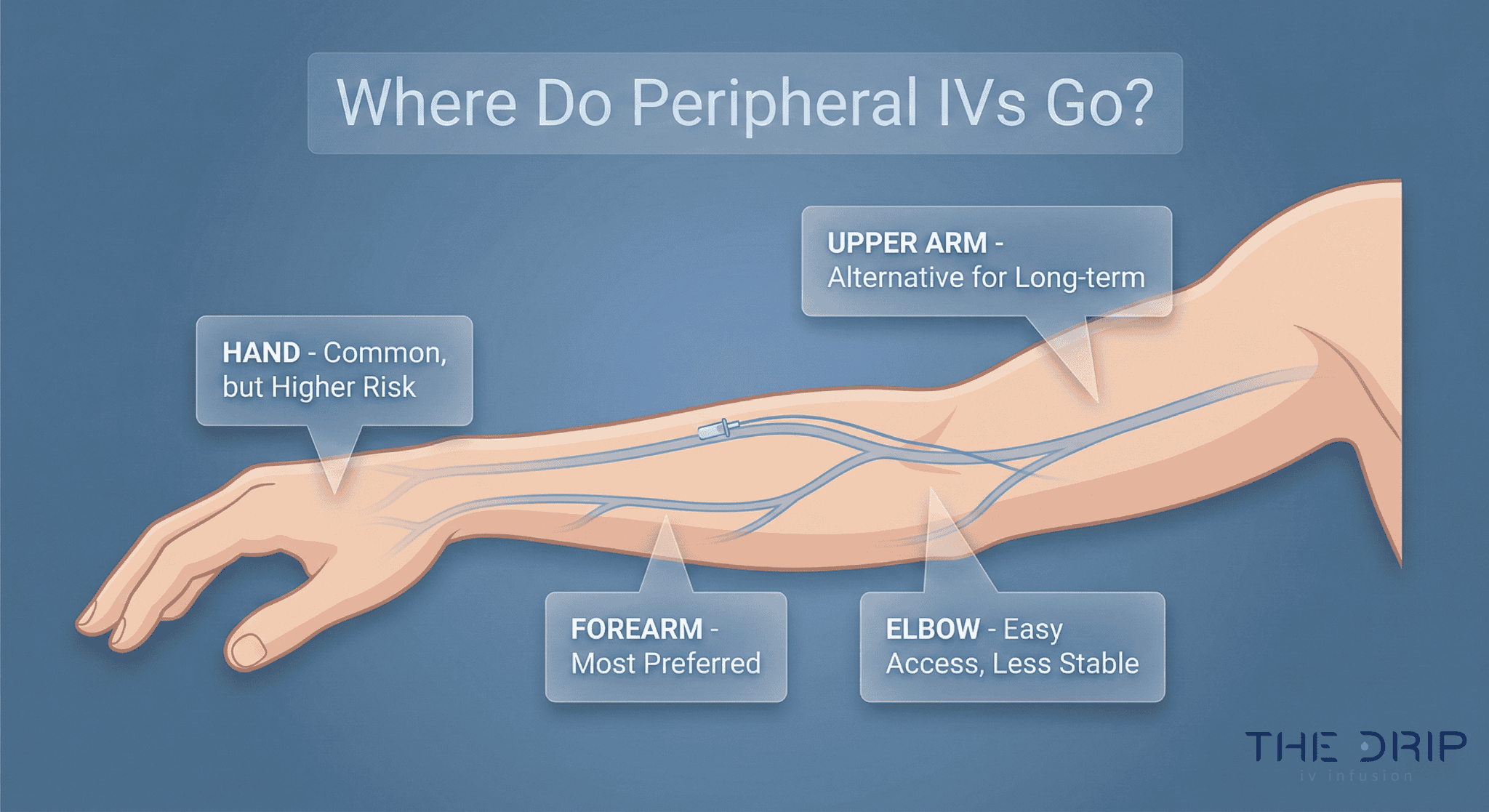
The main IV sites on forearm nurses can choose from are:
Median cubital
Accessory cephalic vein
Basilic vein
Median cubital vein
The most common insertion forearm site may be the median vein, a vein found in the triangular area in the elbow pit.
The median cubital vein is often the preferred site for the administration of IV because it is a superficial vein, meaning it’s close to the skin.
What makes the median cubital a go-to site for nurses is usually that the vein is out of the way of any nerves or bends of the arm. So, patients tend to experience less discomfort as it doesn’t restrict the patient’s movement or cause any pain.
Moreover, by inserting an IV drip through the median cubital vein, nurses reduce the risk of complications. Due to its large size and position, the vein is less prone to some complications like infiltration, which may occur in smaller veins when the nurse takes out the IV catheter after the IV drip has been administered.
Accessory Cephalic Vein
Your next ideal choice when seeking an IV insertion site in the forearm may be the accessory cephalic vein. If the patient’s condition doesn’t allow the insertion into the median cubital, nurses are most likely to opt for the accessory cephalic vein. It’s worth noting that the accessory cephalic vein is found on the lateral aspect of the forearm and upper arm.
You’ll find this vein on the branch that comes off the side of the cephalic vein. As a superficial vein, it is generally highly visible, making the vein one of the top favorite options for medical nurses who administer IV therapy.
Besides visibility, nurses may choose to administer IV therapy in the accessory cephalic vein for various reasons – medical necessity and patient comfort, among the common.
Since the accessory cephalic vein may be found in the triangular area of the elbow, it makes it a good place for inserting a needle as these veins are not subject to pressure or movement.
Moreover, some patients receiving IV therapy may have fragile or collapsible veins, and in such cases, the accessory cephalic vein may be considered as more resilient and a better place to administer IV.

Source: shutterstock.com / Photo Contributor: SeventyFour
Basilic Vein
Another favorable insertion IV site in the forearm is the basilic vein. The vein runs from the palm of the hand and then ascends the medial aspect of the lower arm, reaches the triangular depression in front of the elbow, and moves toward the upper arm. As a superficial vein, the basilic vein is close to the skin, making it more visible and palpable than other veins in the forearm.
The basilic veins are typically larger and more accessible compared to the other superficial veins in the arm, making it a go-to site for nurses when the other veins are less prominent. Due to the vein’s large size, nurses tend to insert IV therapy into this vein, especially if the IV drip contains certain medications, vitamins, or fluid that may irritate or damage smaller veins.
Furthermore, administering IV therapy in the basilic vein may be less painful to the patient, as the vein is not subjected to pressure or movement compared to the veins in the palm or wrist.
Intravenous (IV) Therapy
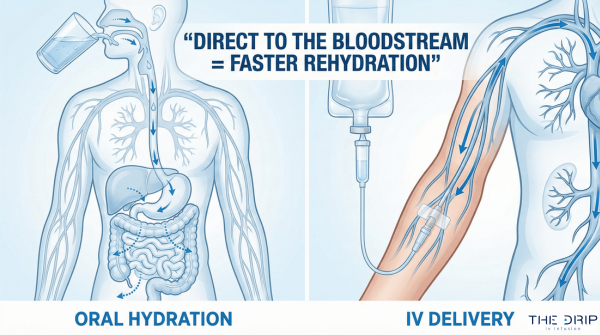
Intravenous therapy, also known as IV therapy, is a medical procedure in which a nurse delivers fluids and medication into the patient’s vein with the help of medical tools. This treatment has become immensely popular in medicine due to its effectiveness, concentrated accuracy, and rapid results.
IV treatments are most common for patients who aren’t able to deliver crucial supplements to their bodies through oral consumption. Since the procedure bypasses the digestive system and delivers fluids straight into the bloodstream, cells can absorb the needed properties at much faster rates than they would otherwise. Because of this, many patients may experience the benefits of IV even in mere minutes.
While IV therapy may be used for treating various conditions, it may also act as a huge boost to a patient’s immune system and overall well-being and health.
Various medications and vitamins can be added to an IV package that may help relieve unpleasant symptoms and discomforts. IV therapy may help you treat nausea, fatigue, morning sickness, vitamin deficiencies, hangovers, and pain, among others.
When receiving an IV treatment, your body will shortly feel effects such as hydration, damaged cell reparation, wound healing, and energy boost.
IV Therapy Benefits
As we said, IV treatments may provide a myriad of benefits and advantages when compared to other types of nutrient administrations. Promoting healthy body functions and helping patients restore their vitamin deficiencies quickly and efficiently is just one of the many perks associated with the administration of IV therapy.
To help regenerate your body, IV drips usually contain vitamins, minerals, and medicine, depending on what you are trying to achieve. The common vitamins and minerals you may find in IV drips are the following:
Vitamin B complex
Vitamin B12
Vitamin C
Zinc
Magnesium
Taurine
Glutathione
Pepcid
Anti-nausea medicine
Anti-pain medicine
Some of the benefits associated with IV therapy worth mentioning are:
IV therapy may be one of the most effective ways to absorb vitamins when compared to oral administration.
This method offers a direct delivery of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals by bypassing the digestive system.
IV may correct vitamin deficiencies or imbalances with accurate and precise dosage.
IV can guarantee a precise delivery of a concentrated dosage of fluids and the correct vitamins or antibiotics into one’s bloodstream.
Each treatment is a customized session with optimum dosage for everyone’s individual needs.
IV is able to provide a sustainable alternative for patients who cannot ingest supplements or have no response to them orally.

Source: shutterstock.com / Photo Contributor: Andrey_Popov
Conclusion
IV therapy is a vital aspect of today’s modern healthcare establishment. It may provide numerous benefits to treat and reduce symptoms of various conditions and health issues. However, choosing the correct IV insertion site is a crucial aspect of gaining the most desirable results from your treatment.
Among the potential IV sites, the forearm is most desirable due to its accessibility, abundance of veins, and patient comfort. The common IV sites on forearm are the median cubital, accessory cephalic vein, and the basilic vein, all located near or pass through the inner elbow pit.