If you’re curious about IV therapy—whether for wellness, medical treatment, or recovery—you’ve come to the right place. We understand you might be wondering if IV therapy is right for your health goals, concerned about safety, or simply want to understand what happens during treatment. Let us guide you through everything you need to know about intravenous therapy, from the science behind it to choosing the right provider.
IV therapy is the direct administration of fluids, vitamins, minerals, or medications into your bloodstream through a vein, bypassing the digestive system to achieve virtually 100% bioavailability. This medical technique has evolved from its origins in hospital settings to include wellness applications, with the global IV hydration therapy market reaching USD 2.64 billion in 2024. Whether you’re considering IV therapy for medical necessity or wellness optimization, understanding the process, benefits, and potential risks will help you make an informed decision about your health.
TL;DR Summary:
- Process & Expectations: IV therapy involves inserting a small needle into your vein to deliver fluids over 10-60 minutes, with sessions typically costing $100-800 depending on the formulation and provider.
- Types Available: Options range from simple hydration therapy and vitamin drips like Myers’ Cocktail to medical treatments including antibiotics, chelation therapy, and total parenteral nutrition (TPN).
- Ingredients & Benefits: Common formulations include B vitamins, vitamin C, magnesium, and calcium, with IV delivery achieving plasma levels up to 100 times higher than oral supplements.
- Equipment & Delivery: Providers use catheters, infusion pumps, and various fluids like saline or dextrose, delivered through peripheral or central IV lines depending on treatment duration.
- Provider Options: IV therapy is available at hospitals, clinics, and through mobile services, with regulations varying by state and no national certification standard.
- Medical Applications: While effective for treating dehydration and delivering medications when oral intake isn’t possible, evidence for wellness benefits in healthy individuals remains limited according to Mayo Clinic experts.
- Benefits vs. Risks: IV therapy offers faster absorption than oral supplements but carries risks including infection, vein irritation, and potential vitamin toxicity if not properly administered.
- Safety Protocols: Legitimate providers follow USP Chapter 797 sterile compounding standards and FDA regulations, with proper licensing required at the state level.
- Insurance & Costs: Medical IV therapy prescribed by physicians may be covered by insurance (71% require prior authorization), while wellness treatments are typically out-of-pocket expenses.
- Getting Started: Choose providers carefully by verifying credentials, asking about safety protocols, and discussing your health history to determine if IV therapy aligns with your wellness goals.
Quick Tip: Before booking any IV therapy session, request to see the provider’s state licensing, ask about their sterile compounding procedures, and verify they maintain proper insurance—these three checks can help you avoid the estimated 38% of facilities that have been cited for safety violations.
How does IV therapy work and what should you expect?
IV therapy works by delivering fluids, vitamins, minerals, or medications directly into your bloodstream through a vein. The process bypasses your digestive system to achieve nearly 100% bioavailability of administered substances. During treatment, a healthcare provider inserts a small catheter into your vein and connects it to an IV bag or syringe containing your prescribed solution. The upcoming sections explain what happens during your session, common uses for IV therapy, and the step-by-step treatment process.
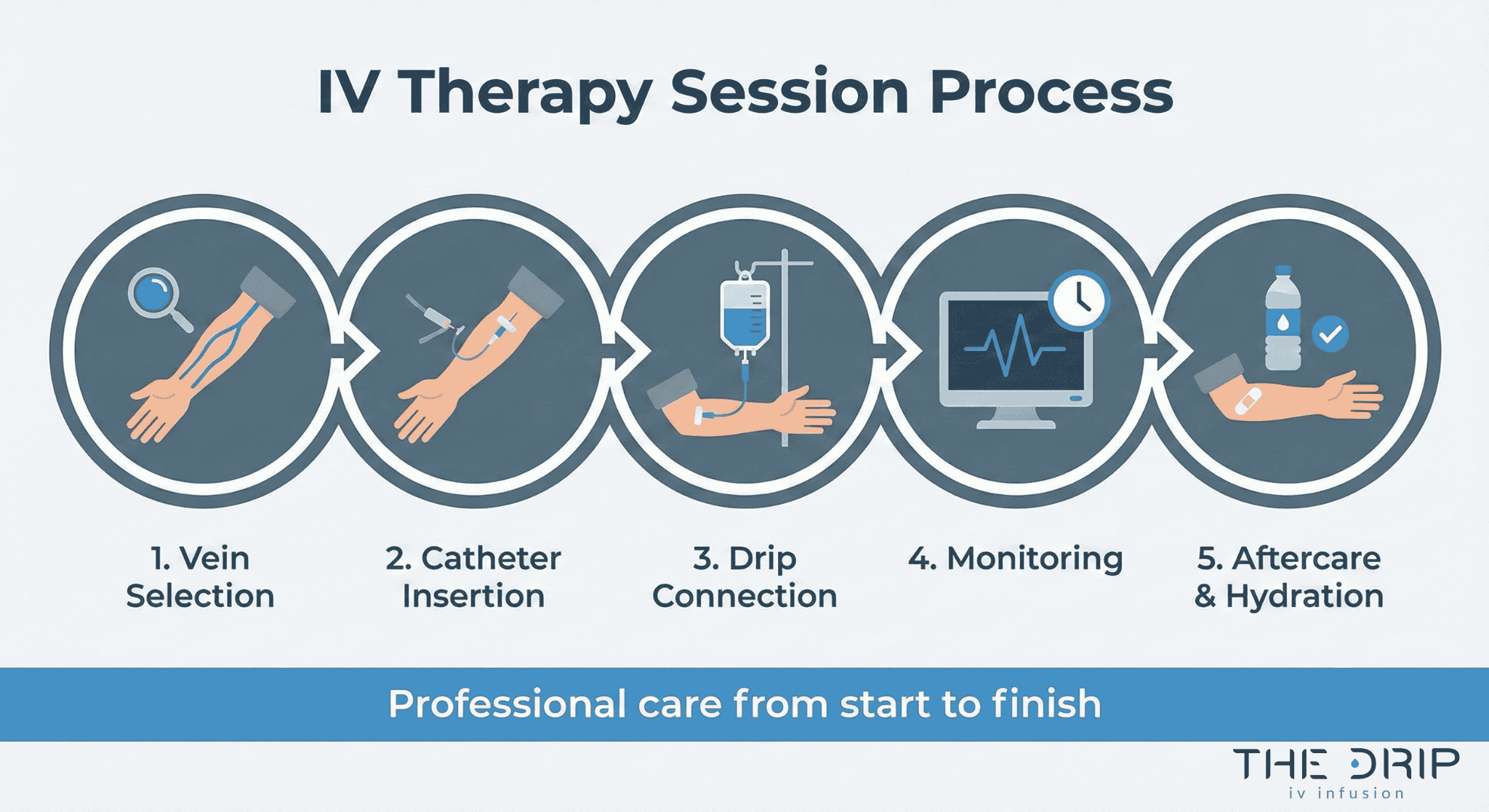
What happens during your IV therapy session?
Your IV therapy session begins when a trained healthcare provider selects an appropriate vein and inserts a needle connected to your IV solution. Myers’ Cocktail, one of the most common vitamin IV formulations, is administered via slow-push infusion over approximately 10 minutes using a 25-gauge butterfly needle. The total solution volume for Myers’ Cocktail is 37 mL of water-soluble vitamins and minerals delivered directly into your bloodstream. Throughout your session, the provider monitors your vital signs and injection site for any adverse reactions. Most sessions last between 20-60 minutes depending on the type and volume of solution being administered.
What is IV therapy used for?
IV therapy is used for both medical treatments and wellness purposes, though coverage differs significantly between these applications. Insurance companies typically cover IV therapy when prescribed by a physician to treat a diagnosed medical condition such as severe dehydration, nutrient deficiencies, or infections requiring intravenous antibiotics. Elective or wellness-based IV therapy is almost never covered by insurance, meaning patients pay out-of-pocket for vitamin drips, hydration therapy, or energy-boosting infusions. The FDA has NOT approved IV vitamin C therapy as a treatment for cancer side effects, despite its widespread promotion for this purpose. Medical uses include treating dehydration, administering medications, correcting electrolyte imbalances, and delivering nutrients to patients who cannot absorb them orally.
How is the IV treatment process done?
The IV treatment process follows a standardized medical protocol to ensure safety and effectiveness. First, your provider reviews your health history and vital signs to determine appropriate treatment. Next, they apply a tourniquet to make your veins more visible and clean the injection site with antiseptic solution. The provider then inserts a sterile needle attached to a catheter into your vein, typically in your arm or hand. Once proper placement is confirmed through blood return, they secure the catheter with medical tape and connect it to your IV bag or syringe. The solution flows into your bloodstream at a controlled rate, either through gravity drip or an electronic infusion pump. After completion, the provider removes the catheter, applies pressure to prevent bleeding, and covers the site with a sterile bandage.
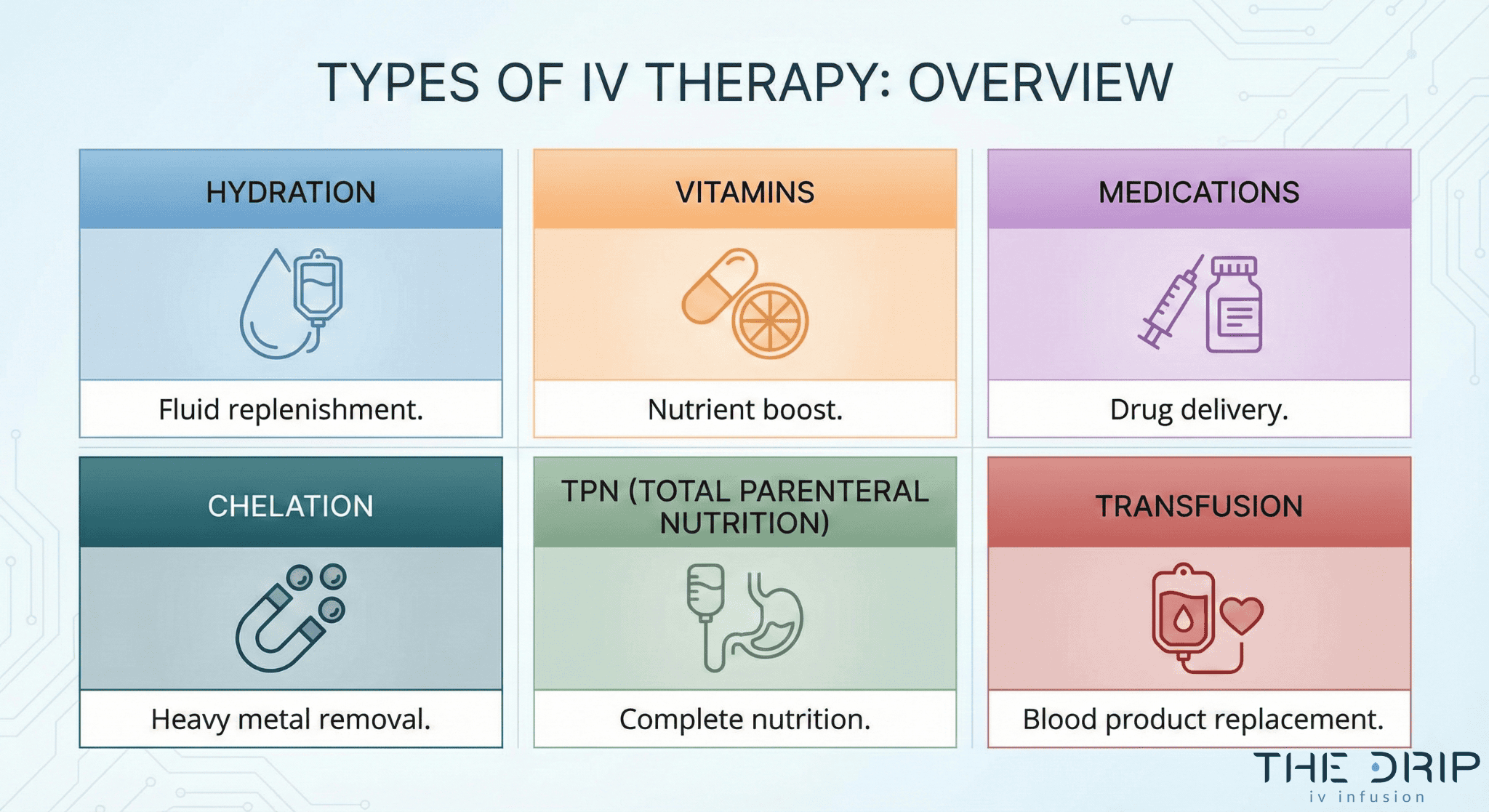
What types of IV therapy can you get?
IV therapy includes six main categories: hydration therapy, vitamin infusions, medication administration, chelation therapy, nutritional support, and blood transfusions. The global IV hydration therapy market reached USD 2.64 billion in 2024, with energy boosters holding the largest segment share at 25.29%.
What is hydration IV therapy?
Hydration IV therapy is the direct administration of fluids and electrolytes into your bloodstream to rapidly restore fluid balance. According to 2024 market data, the global IV hydration therapy market size was USD 2.64 billion, with the energy boosters segment capturing 25.29% market share. Healthcare providers use crystalloid solutions such as normal saline, lactated Ringer’s, and balanced electrolyte formulas to treat dehydration from illness, exercise, or heat exposure. Athletes and wellness clients receive hydration IVs containing sodium, potassium, and magnesium to optimize cellular function and recovery.
What are vitamin IV drips like Myers’ Cocktail?
Vitamin IV drips like Myers’ Cocktail are therapeutic infusions containing water-soluble vitamins and minerals delivered directly into circulation. Myers’ Cocktail contains 5 mL magnesium chloride hexahydrate (20%), 3 mL calcium gluconate (10%), 1 mL hydroxocobalamin (1,000 μg/mL), 1 mL pyridoxine hydrochloride (100 mg/mL), 1 mL dexpanthenol (250 mg/mL), 1 mL B-complex 100, 5 mL vitamin C (500 mg/mL), and 20 mL sterile water. The FDA approved this formulation under Investigational New Drug application IND 66,885, with preparation costs averaging $18 US per dose. Medical facilities administer Myers’ Cocktail for fatigue, migraines, and immune support through slow-push infusion over 10 minutes.
What medications can be given through IV?
Medications that can be given through IV include antibiotics, pain relievers, chemotherapy agents, and biologics requiring direct bloodstream delivery. A 2024 industry analysis revealed that 71% of infusible medications require prior authorization, with average turnaround times spanning 7-14 days. Common IV medications encompass:
- Antibiotics (vancomycin, ceftriaxone, meropenem)
- Pain management drugs (morphine, fentanyl, ketorolac)
- Cardiac medications (amiodarone, diltiazem, epinephrine)
- Anti-nausea agents (ondansetron, metoclopramide)
Healthcare systems rely on IV medication delivery when oral absorption proves inadequate or rapid therapeutic levels are essential.
What is chelation therapy and how does it work?
Chelation therapy is the IV administration of synthetic amino acids that bind to heavy metals in your bloodstream for removal through urination. EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) chelation targets lead, mercury, and cadmium poisoning by forming stable complexes with metal ions. Medical teams administer chelation through slow IV infusion over 1-3 hours, monitoring kidney function throughout treatment. FDA-approved chelation protocols treat verified heavy metal toxicity under strict medical supervision.
What is TPN (total parenteral nutrition) via IV?
TPN (total parenteral nutrition) via IV is complete nutritional support delivered directly into a central vein when the digestive system cannot absorb nutrients. The TPN solution contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and trace elements customized to patient requirements. Hospital teams administer TPN through central venous catheters for patients with bowel obstruction, severe malabsorption, or critical illness requiring 24-hour infusion. Pharmacists compound each TPN bag based on daily laboratory values and metabolic needs.
When might you need a blood transfusion through IV?
You might need a blood transfusion through IV when hemoglobin drops below 7-8 g/dL or during acute blood loss exceeding 30% of blood volume. Medical conditions requiring transfusion include trauma, surgical bleeding, severe anemia, and blood disorders such as sickle cell disease or thalassemia. Blood banks match donor blood type, screen for antibodies, and deliver packed red cells, platelets, or plasma through dedicated IV lines. Transfusion protocols monitor vital signs every 15 minutes to detect adverse reactions.
These IV therapy types serve distinct medical purposes from basic hydration to complex nutritional support, each requiring specific protocols and medical oversight tailored to your health needs.
What vitamins, minerals, and medications are in your IV drip?
IV drips contain varying combinations of vitamins, minerals, and medications depending on their therapeutic purpose. Common formulations include B-complex vitamins, vitamin B12, minerals like magnesium and calcium, and medications ranging from antibiotics to pain relievers. The specific composition determines whether the infusion addresses nutritional deficiencies, treats infections, or manages chronic conditions.
What nutrients are included in vitamin IV therapy?
The nutrients in vitamin IV therapy typically include water-soluble vitamins and essential minerals delivered directly into the bloodstream. B-complex 100 contains 100 mg thiamine HCl, 2 mg riboflavin, 2 mg pyridoxine HCl, 2 mg panthenol, 100 mg niacinamide, and 2% benzyl alcohol as a preservative. Standard formulations incorporate vitamin C at doses ranging from 500 mg to 50 grams, magnesium chloride for muscle function, and calcium gluconate for bone health.
| Ingredient | Form | Dosage |
| B-complex 100 | Thiamine HCl | 100 mg |
| B-complex 100 | Riboflavin | 2 mg |
| B-complex 100 | Pyridoxine HCl | 2 mg |
| B-complex 100 | Niacinamide | 100 mg |
| B-complex 100 | Preservative | 2% benzyl alcohol |
These nutrient combinations target specific health goals through precise dosing unavailable through oral supplementation.
What are the benefits of B12 and NAD+ infusions?
B12 infusions may support energy production, red blood cell formation, and neurological function through direct delivery of hydroxocobalamin or methylcobalamin. Vitamin B12 administered intravenously bypasses gastrointestinal absorption issues that affect up to 30% of older adults. NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) infusions may enhance cellular energy metabolism, DNA repair mechanisms, and mitochondrial function.
NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, potentially contributing to fatigue and cognitive changes. IV administration of NAD+ may restore cellular energy pathways more effectively than oral supplements. Healthcare providers typically recommend these infusions for patients with documented deficiencies or specific metabolic concerns rather than general wellness.
What conditions are treated with IV antibiotics or pain meds?
IV antibiotics treat serious bacterial infections such as sepsis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis that require immediate systemic drug delivery. Common IV antibiotics include vancomycin for MRSA infections, ceftriaxone for respiratory infections, and meropenem for multi-drug resistant organisms. Pain medications administered intravenously include morphine, fentanyl, and ketorolac for post-surgical pain, cancer-related discomfort, or acute injury management.
According to industry data, 71% of infusible medications require prior authorization with average approval times of 7-14 days. IV delivery ensures rapid therapeutic levels for time-sensitive conditions where oral medications prove insufficient. These pharmaceutical infusions require strict medical supervision and dosing protocols to prevent adverse reactions and ensure therapeutic efficacy.
What equipment is used during your IV therapy?
IV therapy equipment consists of specialized medical devices that deliver fluids and medications directly into your bloodstream. The main components include catheters or cannulas for vein access, infusion pumps or drip bags for controlled delivery, and various IV fluids such as saline or dextrose solutions.
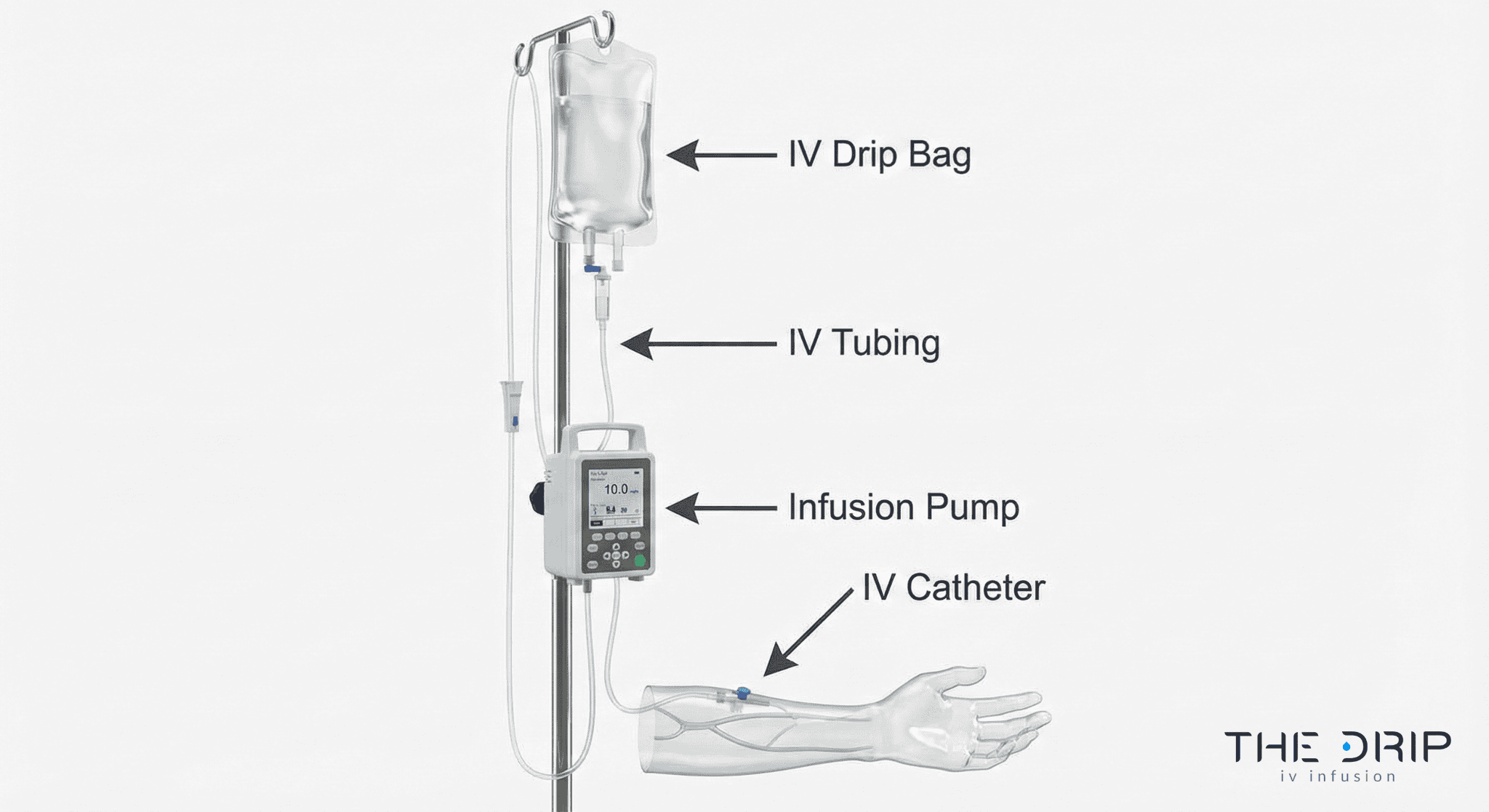
What’s the difference between a catheter, cannula, and IV line?
A catheter is a flexible tube inserted into a vein to deliver IV fluids. An IV cannula is a short, rigid catheter with a plastic hub that remains in the vein after needle removal. The IV line refers to the complete tubing system connecting the fluid bag to the catheter or cannula.
Peripheral IV catheters range from 14-gauge to 24-gauge in diameter. Larger gauges deliver fluids faster but may cause more discomfort during insertion. Central venous catheters extend deeper into major veins near the heart for long-term therapy or irritating medications.
The selection depends on treatment duration, fluid viscosity, and vein condition. Short-term hydration typically uses 20-22 gauge peripheral cannulas, while chemotherapy may require central catheters.
How do infusion pumps and drip bags work?
Infusion pumps are electronic devices that control IV fluid delivery through precise mechanical pressure. These pumps deliver medications at rates from 0.1 mL to 999 mL per hour with accuracy within 5% of the programmed rate.
Gravity drip bags use height and manual flow regulators to control infusion speed. The drip chamber allows visual monitoring of flow rate, typically measured in drops per minute. Standard drip sets deliver 10-20 drops per milliliter.
Smart pumps include dose error reduction systems that alert providers to potential programming errors. Ambulatory pumps allow patient mobility during extended infusions. The choice between pump and gravity depends on required precision, medication type, and treatment setting.
How are different IV fluids like saline and dextrose selected?
IV fluids are selected based on patient hydration status, electrolyte levels, and treatment goals. Normal saline contains 0.9% sodium chloride and treats dehydration and blood loss. Dextrose solutions provide calories and treat hypoglycemia with concentrations ranging from 5% to 50%.
Lactated Ringer’s solution contains sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, and lactate to closely match body fluid composition. Plasma-Lyte provides balanced electrolytes for fluid replacement without lactate.
Hypertonic solutions draw fluid from cells into blood vessels. Hypotonic solutions move fluid from blood into cells. Isotonic solutions maintain fluid balance without cellular shifts. Your provider selects the appropriate fluid based on laboratory values and clinical assessment to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Where can you get IV therapy and who provides it?
IV therapy is available at hospitals, clinics, and homes through various healthcare professionals. Physical providers held a dominant market share of 58.0% in 2024, indicating most patients receive treatment at medical facilities rather than through mobile services. Understanding where and from whom you can receive IV therapy helps ensure safe, effective treatment.
Can you get IV therapy at home, in a clinic, or hospital?
You can get IV therapy at home, in a clinic, or hospital depending on your medical needs and provider availability. Hospitals provide IV therapy for acute medical conditions requiring continuous monitoring. Outpatient clinics offer scheduled treatments for chronic conditions and wellness infusions. Home IV services deliver treatments through mobile nurses or self-administration programs.
A February 2021 case demonstrates home IV therapy risks: a 50-year-old female was hospitalized with suspected septic shock and multi-organ failure after receiving an IV vitamin infusion at home, with blood cultures growing Pseudomonas fluorescens. This contamination case highlights the importance of sterile technique regardless of treatment location.
Medical facilities maintain stricter infection control protocols than home settings. Hospital IV therapy occurs in controlled environments with immediate emergency response capabilities. Clinic-based treatments balance convenience with professional oversight in dedicated infusion centers.
The choice between locations depends on treatment complexity, patient stability, and insurance coverage requirements.
Do nurses or doctors need special training for IV therapy?
Nurses and doctors need special training for IV therapy, though no national certification for IV therapy exists in the United States. IV therapy is regulated at state level, not federally, with each state’s Board of Medicine, Nursing, Pharmacy, and Health setting unique requirements. Training requirements vary significantly between states and provider types.
Registered nurses typically complete IV certification courses covering venipuncture, medication administration, and complication management. Licensed practical nurses may require additional certification depending on state scope of practice laws. Physicians receive IV training during medical school and residency programs.
State boards determine specific competencies required for IV therapy providers. Requirements include documented training hours, supervised practice sessions, and continuing education credits. Some states mandate separate certifications for specialized IV procedures such as PICC line insertion or chemotherapy administration.
Healthcare facilities often impose additional training requirements beyond state minimums to ensure patient safety and reduce liability risks.
What’s the difference between medical and wellness IV providers?
Medical IV providers treat diagnosed conditions under physician oversight while wellness IV providers offer elective treatments for general health optimization. Medical providers include hospitals, infusion centers, and specialty clinics staffed by licensed healthcare professionals treating conditions such as dehydration, infections, or nutritional deficiencies. Wellness providers operate IV drip lounges and mobile services offering vitamin cocktails and hydration therapy.
Medical IV therapy requires physician orders, diagnostic testing, and insurance prior authorization processes. Wellness IV services typically bypass insurance systems, offering cash-pay treatments without formal medical diagnoses. Medical providers follow strict clinical protocols while wellness providers may have more flexibility in formulation choices.
Regulatory oversight differs substantially between provider types, with medical facilities facing comprehensive inspections and wellness clinics operating under varying state regulations.
What are the different ways you can receive IV therapy?
The different ways you can receive IV therapy are through various access points and delivery methods, including peripheral IVs, central lines, PICC lines, and port systems. Healthcare providers select the appropriate IV access based on treatment duration, medication type, and patient needs. Each delivery method offers distinct advantages for specific therapeutic goals, from rapid medication administration to long-term nutritional support.
What’s the difference between IV push and continuous infusion?
IV push and continuous infusion differ in their delivery speed and clinical applications. IV push delivers medication rapidly over 1-15 minutes directly into the vein using a syringe. Continuous infusion administers fluids or medications slowly over hours or days through a drip bag and infusion pump.
IV push suits medications requiring immediate effect, such as emergency drugs, antibiotics, or pain relievers. Healthcare providers use this method when rapid therapeutic levels are essential. The Myers’ Cocktail exemplifies IV push delivery, administered over approximately 10 minutes using a 25-gauge butterfly needle.
Continuous infusion maintains steady medication levels for extended periods. This method delivers chemotherapy, hydration fluids, and critical care medications. Infusion pumps regulate flow rates precisely, preventing concentration fluctuations. Treatment duration ranges from 30 minutes for simple hydration to 24 hours for complex protocols.
What is a PICC line and when is it used?
A PICC line is a peripherally inserted central catheter that extends from an arm vein to the superior vena cava near the heart. Healthcare providers insert PICC lines for treatments lasting weeks to months, eliminating repeated needle sticks. The catheter measures 50-60 centimeters in length and accommodates multiple medication administrations.
Medical teams use PICC lines for:
• Long-term antibiotic therapy (4-12 weeks)
• Chemotherapy administration
• Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
• Frequent blood draws
PICC placement occurs bedside or in radiology using ultrasound guidance. The procedure takes 30-45 minutes under local anesthesia. Patients may maintain PICC lines at home with proper care training. Regular flushing with saline prevents clotting, while sterile dressing changes reduce infection risk.
What are central vs. peripheral IV lines?
Central IV lines access large veins near the heart, while peripheral IV lines enter smaller veins in arms or hands. Central lines include subclavian, internal jugular, and femoral catheters, plus PICC lines and implanted ports. Peripheral IVs use short catheters in superficial veins, typically lasting 72-96 hours.
| Line Type | Insertion Site | Duration | Uses |
| Peripheral IV | Hand, forearm veins | 3-4 days | Short-term hydration, medications |
| Central line | Chest, neck, groin | Weeks to months | Chemotherapy, TPN, long-term antibiotics |
| PICC line | Upper arm | 1-12 months | Home infusions, frequent treatments |
| Port system | Under skin, chest | Years | Cancer treatment, chronic conditions |
Central lines accommodate irritating medications, high-concentration solutions, and rapid fluid resuscitation. These lines require surgical insertion and carry higher infection risks. Peripheral IVs suit most routine treatments, including vitamin infusions and basic hydration therapy.
What medical conditions can IV therapy help you with?
IV therapy delivers fluids, nutrients, and medications directly into the bloodstream to treat various medical conditions. Healthcare providers use intravenous treatment for acute dehydration, infections requiring antibiotics, and chronic conditions needing consistent medication delivery. The direct vascular access bypasses digestive absorption, making IV therapy valuable for patients who cannot take oral medications or need rapid therapeutic effects.
Can IV therapy treat dehydration or infections?
IV therapy treats dehydration by delivering crystalloid solutions such as normal saline, lactated Ringer’s, or dextrose directly into circulation. Severe dehydration from gastroenteritis, heat exhaustion, or excessive fluid loss requires immediate IV fluid replacement to restore blood volume and electrolyte balance. Medical teams administer 1-2 liters of isotonic fluids over 1-4 hours depending on dehydration severity.
IV antibiotics treat serious infections including sepsis, pneumonia, cellulitis, and osteomyelitis. Intravenous delivery achieves therapeutic drug concentrations faster than oral antibiotics, critical for life-threatening infections. Common IV antibiotics include vancomycin for MRSA, ceftriaxone for bacterial meningitis, and piperacillin-tazobactam for hospital-acquired infections.
Healthcare providers monitor fluid intake, urine output, and vital signs during treatment to prevent fluid overload. IV therapy for dehydration and infections requires medical supervision to ensure proper dosing and response.
Is IV therapy helpful for chronic illness or recovery?
IV therapy may support chronic illness management through specialized nutrient protocols. A 2009 study on Myers’ cocktail for fibromyalgia with 34 adults showed significant improvements in pain, depression, and quality of life after 8 weeks, but placebo group also reported significant improvements. This finding suggests both physiological and psychological factors influence perceived benefits.
Chronic conditions potentially benefiting from IV therapy include:
• Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (malabsorption issues)
• Chronic fatigue syndrome (energy support)
• Migraine disorders (magnesium deficiency)
• Cancer treatment side effects (hydration and nutrition)
Post-surgical recovery utilizes IV therapy for pain management, antibiotic prophylaxis, and nutritional support when patients cannot eat normally. Athletes use IV hydration for recovery after endurance events, though medical necessity remains debated. The effectiveness varies significantly based on individual conditions and treatment protocols.
How does IV therapy support surgery, immunity, or energy?
IV therapy supports surgical patients through pre-operative hydration, intraoperative fluid management, and post-operative recovery. Surgeons require patients to fast before procedures, making IV fluids essential for maintaining blood pressure and organ perfusion. Post-surgical IV therapy delivers pain medications, antibiotics, and antiemetics directly while digestive function recovers.
IV administration of vitamin C at doses between 25-50 grams can substantially enhance immune function, reduce inflammation, and reinforce antioxidant defenses. High-dose vitamin C creates pro-oxidant effects at pharmacological concentrations, potentially supporting cancer treatment adjuvant therapy. Immune support protocols often combine vitamin C with zinc, selenium, and B-complex vitamins.
Energy enhancement through IV therapy targets cellular metabolism using B vitamins, magnesium, and amino acids. NAD+ infusions claim to boost mitochondrial function and cellular energy production. These wellness applications lack robust clinical evidence but remain popular among patients seeking fatigue relief.
Understanding which medical conditions benefit from IV therapy helps patients make informed treatment decisions with their healthcare providers.
What are the benefits of getting IV therapy for you?
The benefits of getting IV therapy for you include faster nutrient delivery, superior absorption rates, and targeted support for specific health concerns. IV therapy bypasses digestive limitations by delivering vitamins and minerals directly into your bloodstream, achieving bioavailability rates that oral supplements cannot match. This section explores how IV therapy compares to traditional supplementation methods and examines its potential effects on common wellness goals.
Is IV therapy faster than taking supplements?
IV therapy is faster than taking supplements because it achieves virtually 100% bioavailability by delivering nutrients directly into systemic circulation. When you receive IV therapy, nutrients bypass the digestive system entirely and enter your bloodstream immediately. This direct delivery method eliminates the 2-4 hour absorption period required for oral supplements to pass through your stomach and intestines.
The speed advantage becomes particularly significant when rapid rehydration or nutrient replenishment is needed. IV fluids can restore hydration levels within 30-60 minutes, while oral rehydration may take several hours to achieve similar results.
Does IV therapy offer better absorption?
IV therapy offers better absorption than oral supplementation, particularly for water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C. High-dose IV vitamin C can achieve plasma levels up to 100 times higher than oral administration. This dramatic difference occurs because oral vitamin C intake exceeding approximately 1 gram results in significantly diminished absorption due to limited intestinal transporter capacity.
The absorption advantage extends to other nutrients as well. B vitamins, magnesium, and amino acids delivered intravenously avoid the variable absorption rates associated with digestive health, medication interactions, and genetic factors that affect oral supplementation. This complete absorption allows healthcare providers to deliver precise therapeutic doses.
Can IV therapy help with fatigue, immunity, or hangovers?
IV therapy may help with fatigue, immunity, or hangovers, though scientific evidence remains limited for wellness applications. According to Dr. Brent A. Bauer, M.D., Director of Research at Mayo Clinic, “There is limited evidence that IV vitamins provide benefit to people with normal nutritional intake and levels.”
Despite limited clinical evidence, many patients report subjective improvements in energy levels and recovery times following IV therapy sessions. The immediate hydration and electrolyte replenishment provided by IV fluids may contribute to these perceived benefits, particularly in cases of mild dehydration or electrolyte imbalance.
The next section examines potential risks and side effects you should understand before considering IV therapy, including common adverse reactions and important safety considerations for specific health conditions.
What are the risks and side effects you should know about IV therapy?
The risks and side effects of IV therapy include kidney damage, infections, and complications from contaminated products. A 2016 oncology practice case exposed 38 patients to contaminated IV therapy, resulting in 17 infections with Exophiala dermitides. Understanding these risks helps you make informed decisions about IV treatment safety.
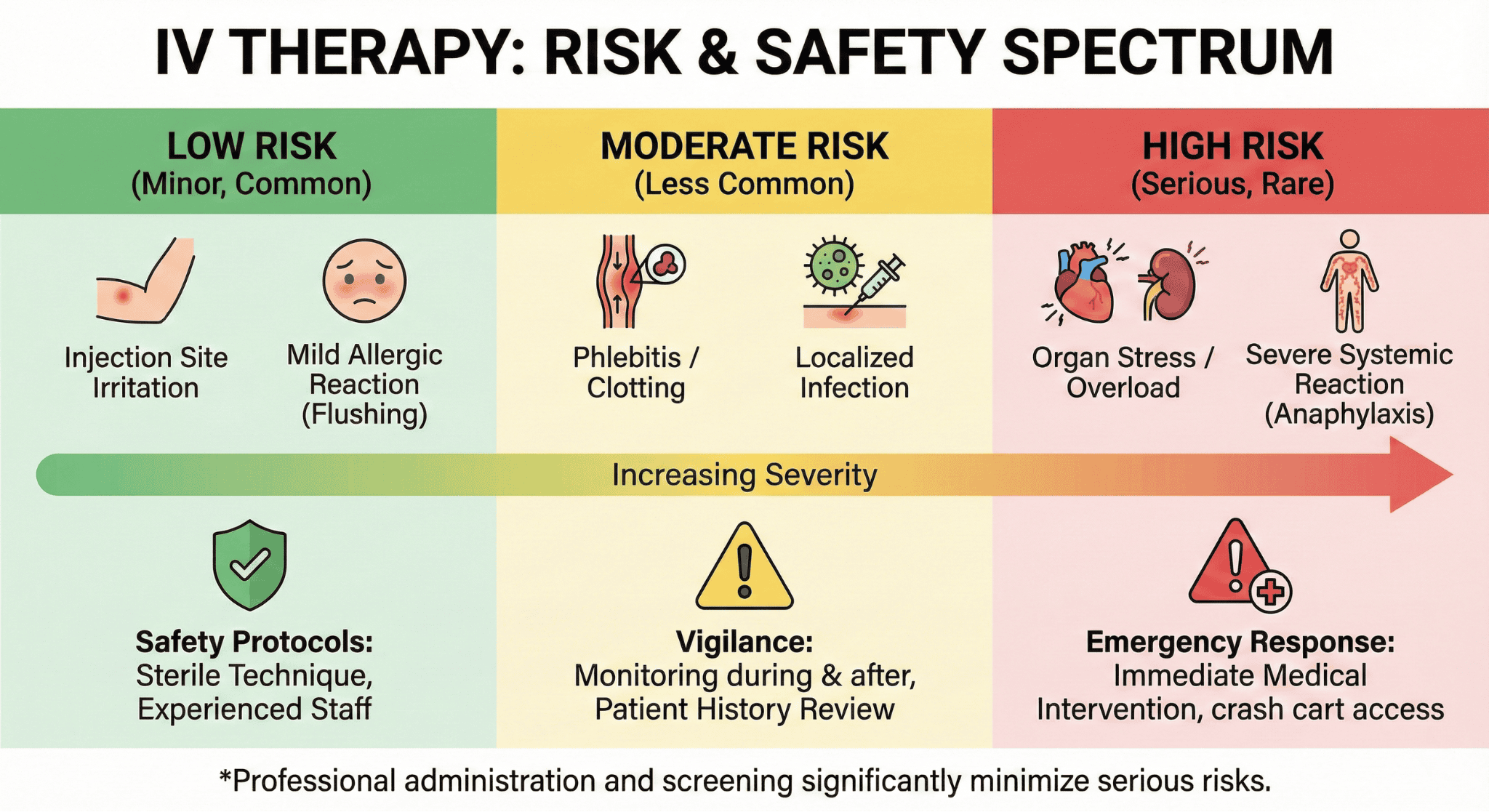
What are the most common side effects of IV drips?
The most common side effects of IV drips are kidney damage, heart rhythm abnormalities, blood pressure changes, gastrointestinal symptoms, and peripheral nerve damage. Dr. Brent A. Bauer from Mayo Clinic states that high doses of certain vitamins and minerals have been linked to these adverse effects.
Common side effects occur in two categories:
• Immediate reactions: Pain at injection site, vein irritation, and allergic responses
• Systemic effects: Nausea, headaches, dizziness, and electrolyte imbalances
• Organ-specific impacts: Kidney stress from high-dose vitamin C and liver burden from excessive B vitamins
• Cardiovascular changes: Blood pressure fluctuations and irregular heartbeat from rapid mineral infusions
The severity depends on infusion rate, concentration, and individual tolerance. These effects underscore why medical supervision remains essential for IV vitamin therapy.
Can IV therapy cause infections or complications?
IV therapy can cause infections and complications through contaminated products or improper administration. A 2016 case at an oncology medical practice infected 17 of 38 exposed patients with Exophiala dermitides, a thermophilic black yeast, due to a contaminated compounding environment.
The FDA warns that contaminated or poor-quality compounded drug products can lead to serious patient illnesses, including death. Infection risks include:
• Bacterial contamination: Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus species
• Fungal infections: Yeast and mold exposure from non-sterile environments
• Bloodstream infections: Sepsis risk from contaminated IV lines
• Site complications: Phlebitis, infiltration, and abscess formation
Proper sterile technique and USP 797 compliance reduce these risks significantly. These complications highlight the importance of choosing certified IV therapy providers.
Who should avoid IV therapy?
People who should avoid IV therapy include those with advanced kidney disease, heart failure, and history of severe allergic reactions to vitamins or medications. Primary contraindications exist for specific medical conditions that make IV therapy dangerous.
| Condition | Risk Factor | Specific Concern |
| Kidney Disease | High | Inability to filter excess vitamins and minerals |
| Heart Failure | High | Fluid overload from IV volume |
| Allergies | Variable | Anaphylactic reactions to vitamin compounds |
| Pregnancy | Moderate | Limited safety data for high-dose vitamins |
Additional risk groups include patients on anticoagulants, those with G6PD deficiency, and individuals with active infections. Medical screening before IV therapy identifies these contraindications and prevents adverse events in vulnerable populations.
What safety measures protect you during IV therapy?
IV therapy safety measures include strict infection control protocols, continuous monitoring systems, and sterile compounding standards that protect patients throughout treatment. Healthcare providers follow USP Chapter 797 guidelines and federal regulations to ensure each infusion meets pharmaceutical-grade safety requirements. The following protocols minimize risks and maintain treatment integrity.
How do providers prevent infection with IVs?
Providers prevent IV infections through aseptic technique, sterile equipment, and controlled environments. IV hydration clinics must comply with USP Chapter 797 standards for sterile compounding, which mandate ISO-5 classified clean rooms, proper personnel garbing, and validated sterilization procedures.
A July 2020 FDA inspection at The Guyer Institute revealed critical violations when personnel in street clothes with ungloved hands filled sterile drug products outside the ISO-5 area. These lapses demonstrate why strict adherence to sterile protocols remains essential.
Prevention measures include:
- Hand hygiene with antimicrobial soap before and after patient contact
- Sterile gloves and masks during IV insertion
- Skin antisepsis using 2% chlorhexidine or 70% isopropyl alcohol
- Single-use needles and catheters
- Covered IV sites with transparent sterile dressings
Staff training on infection control updates quarterly to maintain competency.
How is your IV site monitored for issues?
Your IV site undergoes continuous monitoring through visual inspection, patient feedback, and documented assessments every 30-60 minutes. Trained nurses check for infiltration, phlebitis, and infection signs including redness, swelling, pain, or leakage around the insertion point.
Monitoring protocols include temperature checks, flow rate verification, and catheter positioning assessment. Electronic infusion pumps track delivery rates and alert staff to occlusions or air bubbles.
Signs requiring immediate intervention:
- Burning sensation at the IV site
- Visible swelling or skin tightness
- Cool skin temperature near insertion
- Slowed or stopped infusion flow
Documentation captures each assessment with timestamps and observations. This systematic approach enables early detection and intervention before complications develop.
What protocols are followed to ensure sterility?
Sterility protocols encompass environmental controls, equipment preparation, and regulatory compliance throughout the IV therapy process. IV hydration clinics must comply with Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, which establishes pharmaceutical compounding standards.
| Item | Requirement | Spec | Source/Year |
| Clean room | Air changes | 20+ per hour | USP 797 |
| Work surface | Disinfection frequency | Every 30 minutes | USP 797 |
| Compounding area | Particle count | <3,520 particles/m³ | ISO-5 2024 |
| Staff garbing | Components | Sterile gloves, masks, gowns | FDA 2023 |
Quality assurance includes batch testing, expiration dating, and storage temperature monitoring. Environmental sampling occurs monthly to verify sterility maintenance. These multilayered protocols create redundant safeguards that protect patient safety throughout IV therapy delivery.
How should you prepare for your IV therapy appointment?
Preparing for your IV therapy appointment involves hydration, documentation, and communication with your provider. A 2019 survey by the Infusion Nurses Society found that 78% of successful IV insertions occurred in well-hydrated patients on the first attempt. The following steps ensure your body is ready for treatment and your provider has essential information for safe administration.
What should you do before getting IV therapy?
Before getting IV therapy, you should hydrate by drinking 16-24 ounces of water, eat a light meal, and wear loose clothing. According to a 2020 clinical guideline from the Association for Vascular Access, proper hydration increases vein visibility by 23% and reduces insertion attempts.
Arrive 15 minutes early to complete paperwork and avoid caffeine or alcohol 24 hours before treatment. Bring a list of current medications, supplements, and recent lab results if available.
The preparation phase determines IV placement success and minimizes complications during your session.
What questions should you ask your provider?
The questions you should ask your provider include certification status, sterile compounding protocols, emergency procedures, and expected outcomes. Request specific information about USP 797 compliance, staff training credentials, and adverse reaction protocols.
Essential questions to cover:
- What certifications do your IV therapy nurses hold?
- How do you ensure sterility during preparation?
- What emergency equipment is available on-site?
- How many treatments will I need for my goals?
A 2021 patient safety report from the Institute for Safe Medication Practices emphasized that informed patients experience 41% fewer adverse events. Document your provider’s answers and request written information about your specific IV formulation.
Understanding your provider’s qualifications and safety measures helps you make informed decisions about treatment.
What kind of health history should you share?
The health history you should share includes all medical conditions, allergies, medications, and previous IV therapy experiences. According to a 2018 study in the Journal of Infusion Nursing on patient screening protocols, complete health histories prevented 89% of potential drug interactions in IV therapy settings.
Disclose these critical details:
- Kidney disease, heart conditions, or blood disorders
- Allergies to medications, adhesives, or latex
- Current prescriptions and over-the-counter supplements
- Previous reactions to IV treatments or injections
- Recent surgeries or hospitalizations
Include pregnancy status, breastfeeding, and any planned medical procedures within 30 days. Providers need this information to select appropriate formulations and monitor for contraindications.
Complete health disclosure enables your provider to customize treatment and prevent complications specific to your medical profile.
What should you expect after your IV therapy session?
After your IV therapy session, you can expect varying onset times for effects depending on the type of infusion received. Most patients experience immediate hydration benefits, while vitamin and mineral effects develop over hours to days. Understanding proper aftercare and warning signs helps ensure safe recovery from your treatment.
How long does it take to feel the effects?
The time to feel effects from IV therapy varies based on the specific treatment administered. Hydration therapy provides immediate relief, with patients typically feeling rehydrated within 30-60 minutes as fluids directly enter the bloodstream. Vitamin infusions like Myers’ Cocktail may produce initial energy improvements within 2-4 hours, though full benefits often develop over 24-72 hours as cells utilize the nutrients.
NAD+ infusions may require 4-6 hours for initial cognitive clarity, with peak effects occurring 1-2 days post-treatment. Antibiotic IV therapy follows pharmacokinetic patterns specific to each medication, with therapeutic levels typically achieved within 1-2 hours. Individual factors affecting onset include baseline nutritional status, metabolic rate, and severity of the condition being treated.
What aftercare is needed after an infusion?
Aftercare following an infusion requires monitoring the insertion site and maintaining proper hydration. Keep the bandage on the IV site for at least 30 minutes to prevent bleeding, then check for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or discharge over the next 24-48 hours. Drink 16-24 ounces of water within two hours post-treatment to support continued hydration and nutrient distribution.
Avoid strenuous exercise for 4-6 hours after treatment to allow your body to process the infused nutrients. Some providers recommend eating a light meal within an hour if you received high-dose vitamin C or B-complex vitamins to prevent mild nausea. Document any unusual symptoms in a journal, noting time of onset and severity for discussion with your provider.
When should you contact your provider after IV therapy?
Contact your provider immediately if you experience severe symptoms after IV therapy. Warning signs requiring urgent attention include difficulty breathing, chest pain, severe headache, or signs of allergic reaction such as hives, swelling, or throat tightness. Infection indicators at the IV site—including increasing pain, red streaking, pus, or fever above 100.4°F—warrant immediate medical evaluation.
Non-emergency situations still requiring provider contact include persistent nausea lasting over 24 hours, unusual bruising extending beyond the insertion site, or numbness and tingling in extremities. Additionally, notify your provider if expected benefits don’t materialize within the timeframe discussed during your consultation, as this may indicate need for dosage adjustment or alternative treatment approaches.
Understanding post-treatment expectations and maintaining open communication with your IV therapy provider ensures optimal outcomes and early intervention if complications arise.
Who regulates and oversees IV therapy for your safety?
IV therapy regulation occurs primarily at the state level through each state’s Board of Medicine, Nursing, Pharmacy, and Health, with no single federal oversight body governing all IV therapy practices. The FDA regulates IV medications and equipment, while state boards establish licensing requirements for practitioners and facilities. IV hydration clinics must comply with USP Chapter 797 standards for sterile compounding and Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
What licenses or certifications should your IV provider have?
Your IV provider should hold an active medical license (MD, DO, NP, or PA) or nursing license (RN) in the state where they practice. No national certification for IV therapy exists. State requirements vary significantly—some states require additional IV therapy certification courses, while others consider IV administration within basic nursing or medical scope of practice.
Healthcare providers administering IV therapy typically need:
- Active state medical or nursing license
- Current CPR/BLS certification
- Malpractice insurance coverage
- State-specific IV therapy training (where required)
Facilities offering IV therapy should maintain business licenses, health department permits, and comply with local zoning regulations. Medical directors overseeing IV clinics need physician licenses and may require additional administrative credentials.
What are the legal and safety standards for IV therapy?
Legal standards for IV therapy include compliance with USP Chapter 797 for sterile compounding and adherence to state practice acts defining scope of care. Safety standards require proper patient screening, informed consent documentation, and emergency response protocols.
A July 2020 FDA inspection at The Guyer Institute revealed critical violations: personnel in street clothes with ungloved hands filling sterile drug products outside ISO-5 areas. These violations demonstrate why strict adherence to sterility standards prevents contamination.
Key safety requirements include:
- Sterile compounding in ISO-5 classified environments
- Written protocols for adverse reactions
- Proper medication storage and handling
- Patient assessment and monitoring procedures
- Documentation of all treatments and outcomes
The FDA Statement warns: “Contaminated, or otherwise poor quality, compounded drug products can lead to serious patient illnesses, including death.” This underscores why providers must follow established safety protocols consistently.
Are there state or federal regulations for IV clinics?
IV therapy is regulated at state level, not federally; each state’s Board of Medicine, Nursing, Pharmacy, and Health sets unique requirements. Federal oversight applies only to specific aspects: FDA regulates medications and devices, while CMS governs Medicare/Medicaid reimbursement for medical IV therapy.
State regulations typically address:
- Practitioner licensing and supervision requirements
- Facility registration and inspection standards
- Prescription requirements for IV medications
- Medical director oversight obligations
A February 2021 inspection at Age Management Institute Santa Barbara found lack of certified ISO-5 classified area, peeling paint, stained work surfaces, visibly dirty equipment, and air vents with dust and grime. These conditions violated both state health codes and federal compounding standards.
IV clinics must comply with Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act when compounding sterile preparations. State boards conduct inspections and can impose penalties ranging from warnings to license revocation for violations.
Understanding your state’s specific regulations helps you verify whether your IV provider operates legally and maintains proper safety standards for your protection.
How can you choose the right IV therapy provider?
Choosing the right IV therapy provider requires evaluating clinical standards, verifying credentials, and recognizing warning signs of unsafe practices. Your provider should maintain sterile compounding areas, employ licensed medical professionals, and follow FDA regulations for patient safety.
What should you look for in an IV drip clinic?
An IV drip clinic should have a certified ISO-5 classified area for sterile compounding, licensed medical staff, and transparent pricing. Check for state medical board licenses displayed in the facility. The clinic must comply with USP Chapter 797 standards for sterile preparation and Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
Professional clinics maintain clean environments with properly sealed surfaces, HEPA-filtered air systems, and staff wearing appropriate protective equipment. Request to see their compounding area and verify their insurance coverage for medical procedures.
How do you know if your IV provider is legitimate?
Your IV provider is legitimate when they hold active state licenses, require medical history reviews, and perform health assessments before treatment. Legitimate providers display credentials from their state Board of Medicine, Nursing, or Pharmacy. They document allergies, medications, and medical conditions before administering any IV therapy.
Verified providers explain risks, benefits, and costs upfront. They use FDA-approved equipment and maintain patient records according to HIPAA standards. Ask for their National Provider Identifier (NPI) number and verify it through the NPPES database.
What red flags should you watch out for?
Red flags include lack of certified ISO-5 classified areas, peeling paint, stained work surfaces, visibly dirty equipment, and air vents with dust and grime. A 2021 inspection at Age Management Institute Santa Barbara revealed these exact violations, demonstrating unsafe compounding conditions.
Avoid clinics that skip health screenings, promise unrealistic results, or operate without medical oversight. Unlicensed staff administering IVs, reused equipment, and facilities that refuse to show credentials signal immediate danger. Report suspicious practices to your state medical board immediately.
How much will IV therapy cost you?
IV therapy costs vary significantly based on treatment type, provider location, and insurance coverage. Individual sessions typically range from $100 to over $300, with specialized formulations reaching $800 per treatment. Understanding pricing factors helps you budget for treatment and identify potential insurance benefits or financial assistance programs.
What is the average price of an IV drip session?
The average price of an IV drip session ranges from $100 to over $300, depending on formulation and provider. Basic hydration treatments start around $100, while complex vitamin cocktails cost $250 to $800 for a single treatment. Specialty infusions containing NAD+, high-dose vitamin C, or prescription medications command premium prices due to ingredient costs and administration complexity. Urban wellness centers charge 20-40% more than suburban clinics for identical treatments.
Is IV therapy ever covered by insurance?
IV therapy is covered by insurance when medically necessary and prescribed by a physician. According to AmeriPharma data, insurance companies approve 81% of prior authorization requests for medically indicated IV treatments. AmeriPharma secured over $55 million in financial assistance for patients requiring ongoing infusion therapy. Coverage typically includes IV antibiotics, chemotherapy, and treatments for diagnosed conditions such as dehydration, malnutrition, or chronic illness. Wellness and elective IV treatments remain excluded from standard insurance benefits.
What factors affect the total cost of your IV therapy?
The total cost of your IV therapy depends on treatment complexity, provider credentials, and session frequency. Premium ingredients like NAD+ or glutathione add $100-300 per session. Board-certified physicians charge higher rates than nurse practitioners or registered nurses. Package deals reduce per-session costs by 15-30% for multiple treatments. Additional factors influencing price include clinic overhead, geographic location, and whether treatments occur in-clinic or through mobile services. Understanding these variables helps you compare providers and maximize value when selecting IV therapy options.
How should you get started with IV therapy?
Getting started with IV therapy requires selecting a qualified provider and understanding treatment options. The Drip IV Infusion offers personalized consultations to match patients with appropriate vitamin infusions based on individual health needs. Consider your wellness goals, medical history, and budget when exploring IV therapy options.
Can The Drip IV Infusion help you choose the right IV drip for your needs?
The Drip IV Infusion can help you choose the right IV drip for your needs through personalized consultation services. A clinical survey demonstrates that patients are generally satisfied with receiving infusions when properly matched to their health requirements. Most patients and relatives surveyed accepted and were in favor of intravenous hydration, indicating strong treatment acceptance rates.
The Drip IV Infusion’s trained professionals assess individual hydration levels, nutritional deficiencies, and wellness objectives before recommending specific formulations. This personalized approach ensures patients receive targeted vitamin and mineral combinations that address their unique health concerns.
What are the key takeaways you should remember about IV therapy?
The key takeaways about IV therapy include its substantial market growth and increasing consumer adoption. Intravenous therapy brought in $2.1 billion in revenue in the U.S. in 2024, demonstrating widespread acceptance of this wellness treatment. The market is projected to reach USD 5.66 billion by 2033 with a compound annual growth rate of 9.0% from 2025 to 2033.
North America dominated the market with 46.8% share in 2024, reflecting strong regional demand for IV wellness services. These statistics indicate IV therapy has evolved from purely medical treatment to mainstream wellness options. Understanding market trends helps patients recognize IV therapy as an established healthcare service with growing professional oversight and standardization.
