Vitamin B12 therapy is quite popular among patients who have a deficiency of this vitamin or specific health conditions. Vitamin B12 is known to participate in many metabolic processes important for general health, so it is important to establish a normal balance in the body. To achieve such a balance, many opt for Vitamin B12 Injection IV or IM.
So, what is the most effective way to get the benefits that B12 has to offer? Keep reading as you will learn about intravenous and intramuscular therapy, their differences, modes of action, and advantages.

Source: shutterstock.com / Photo Contributor: Arnon Thongkonghan
Which One Is Better– Vitamin B12 Injection IV or IM
Generally speaking, there are several ways of getting vitamin B12 into the body. Depending on the method you choose to receive the vitamin B12, you’ll get different effects of the vitamin. But which one is a better choice when it comes to this particular vitamin– vitamin B12 injection IV or IM? What is the difference between the two?
Vitamin B12 IV (intravenous) administration
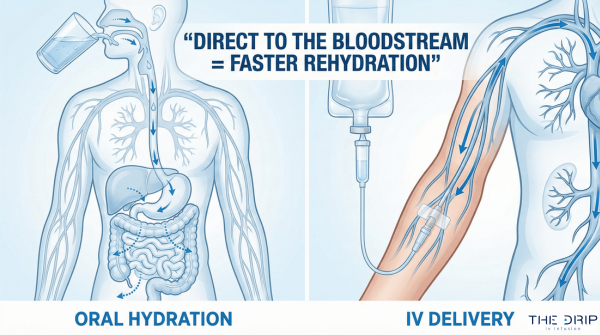
With this method of administration, the vitamin is directly introduced into a vein, that is, into the bloodstream. The IV fluid content is drawn down the IV tubing to the catheter, directly entering the bloodstream and bypassing the digestive system, which allows you to feel the effects almost instantly.
The positive side of this way of administering B12 is that the digestive system is bypassed with IV therapy. Introducing the IV fluid directly into the bloodstream makes maximum absorption of nutrients, minerals, and vitamins possible.
However, regarding the duration of the effect, the IV therapy is shorter than the IM injection. This is because the content delivered via IM therapy takes time to pass from the muscles into the bloodstream.
With the various advancements in the medical field, in addition to healthcare facilities, you can now get at-home IV therapy service in Queen Creek.
Vitamin B12 IM (intramuscular) administration
The intramuscular route of B12 administration significantly differs from IV therapy. First of all, as the term itself suggests, IM injections are given intramuscularly, as opposed to IV therapy, where vitamin B12 is administered directly into the bloodstream. This type of administration is used to deliver vitamin B12 deep into your muscles to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Such IM injections are usually administered either into the upper arm or buttocks. The reason why these body parts are chosen for IM is because of the muscle mass they contain. That way, the contents of an IM injection can be more effective and reach the bloodstream more quickly. In contrast, if administered into a layer of subcutaneous fat, the administration of IM may not work, as fat has little access to the bloodstream.
Such IM injections usually contain vitamin B12 as either cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin. Unlike intravenous therapy, with intramuscular administration, you don’t feel the effects immediately, but the contents stay in your body longer.
Administration Procedures and Frequency
As mentioned before, IV therapy and IM administration differ in performance and the time of action. Regardless of whether it is intravenous therapy or intramuscular injection, you should talk to a licensed medical professional. The medical doctor should be informed of your medical history, the current medications you are taking, and allergic reactions, if you have some, that is.
Furthermore, you should familiarize yourself with the procedure, what are the potential benefits and possible side effects.
Procedure and process for IV B12 injections
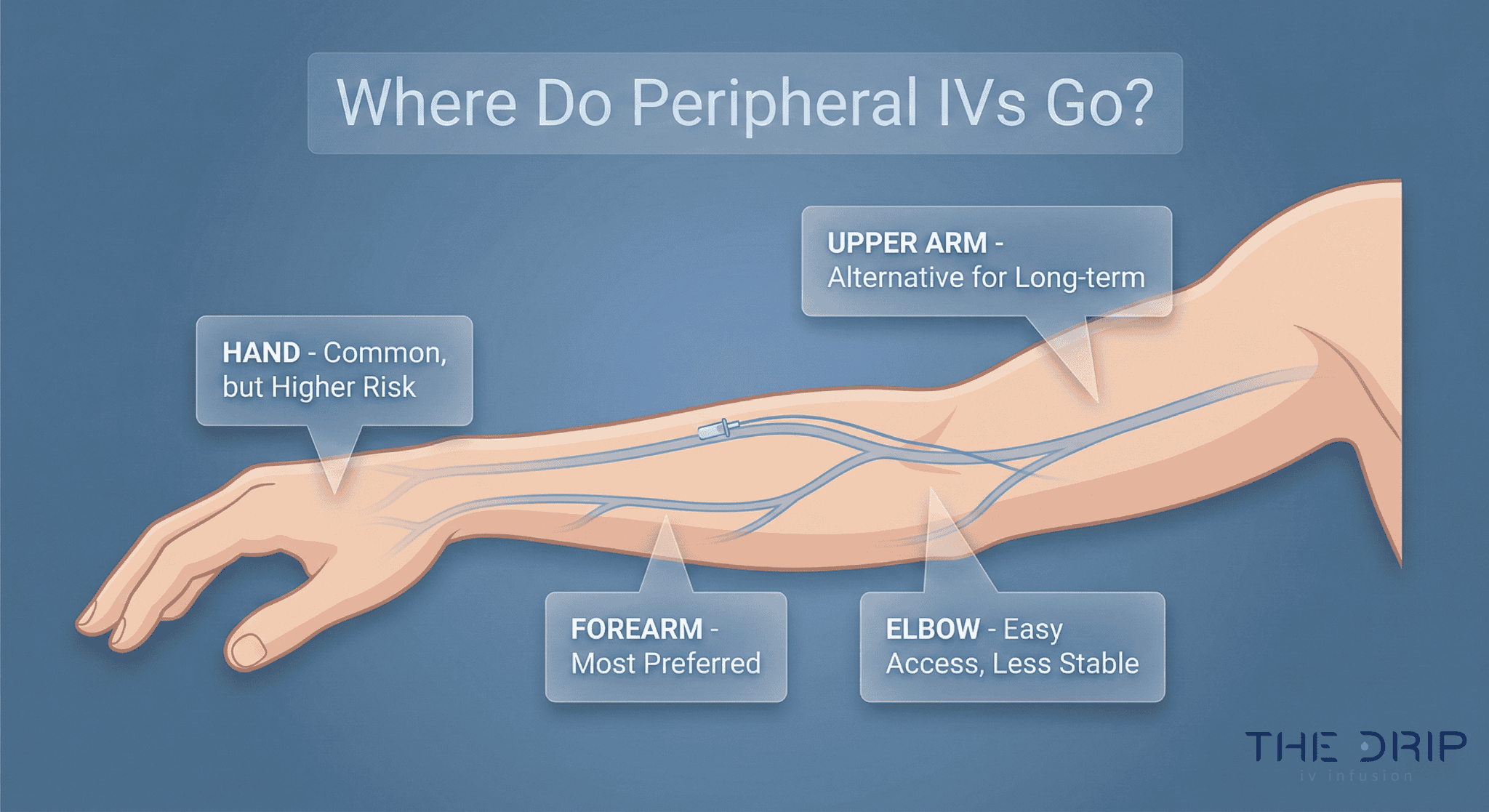
So, what is the procedure for B12 IV therapy? To perform the procedure successfully, a nurse inserts a small catheter into the vein, which will allow the IV fluid to be transported from the IV bag.
After this step, the tube is connected to the IV fluid bag, usually located above the patient’s head. At the base of the IV bag is a nozzle that controls the amount of IV fluid passing through the tube.
Procedure and process for IM B12 injections
The nurse will determine an injection site after you are familiar with the whole process. There are usually four sites for B12 administration: the thigh, outer hip, upper arm, and buttock. Choosing the ideal injection site usually depends on the patient’s age and comfort level. These are the steps for intramuscular administration of B12:
Cleaning the injection site with cotton and alcohol
Preparation of the injection (inserting the needle into the vial and withdrawing the plunger; pushing the plunger carefully so that there are no air bubbles)
Inserting the needle at a 90-degree angle and pressing the plunger to apply the contents.
Cleaning the place with alcohol and applying a bandage.

Source: shutterstock.com / Photo Contributor: Arina_C
Cost Comparison
Regarding the cost of IV therapy and intramuscular injection, health insurance usually does not cover these procedures. However, the cost of such treatments can vary from state to state and where they are administered.
Regarding IM injections, they may be covered by health insurance if they are part of the therapy for specific diseases such as anemia, neuropathies, or gastrointestinal diseases.
Conclusion
There are different conditions when vitamin B12 injection IV or IM should be taken. Usually, IV therapy is used if the effect of the IV fluid needs to be achieved quickly, while in the case of intramuscular injection, the vitamin remains in the body for a longer time.
Please note that these procedures are not intended to replace any regular therapy or medication prescribed by a physician. Therefore, if you think you are an ideal candidate for any of these procedures, a consultation with a medical professional is of utmost importance.